108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

罗库溴铵对接受选择性单侧全膝关节置换术患者止血带引起的骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用:一项前瞻性、双盲、随机对照研究
Authors Chen H, Wei JQ, Wang YW, Zhou KP, He Y, Liu H, Zhang YY
Received 8 March 2020
Accepted for publication 26 July 2020
Published 18 August 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 3373—3384
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S252546
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Georgios D. Panos
Purpose: To investigate the effects of different doses of rocuronium on ischemia-reperfusion injury in skeletal muscle induced by tourniquet in patients undergoing elective unilateral total knee arthroplasty.
Patients and Methods: A total of 90 patients undergoing elective unilateral knee arthroplasty under general anesthesia combined with femoral nerve block were randomly divided into 3 groups: normal saline group (group S), rocuronium 0.6 mg/kg group (group L), and rocuronium 1.2 mg/kg group (group H). The primary outcome was the expression of dystrophin in skeletal muscle at 60 min after ischemia. Secondary outcomes included the concentration of malondialdehyde (MDA) and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) in blood at 5 min and 30 min after reperfusion. In addition, thigh girth at 24 h and 48 h after operation, the leaving bed time, the incidence of tourniquet-related hypertension and short-term (3 days after operation) complications (nausea and vomiting, swelling, blister, wound infection) and long-term (3 months after operation) complications (joint instability, stiffness, nerve paralysis, pain) were recorded.
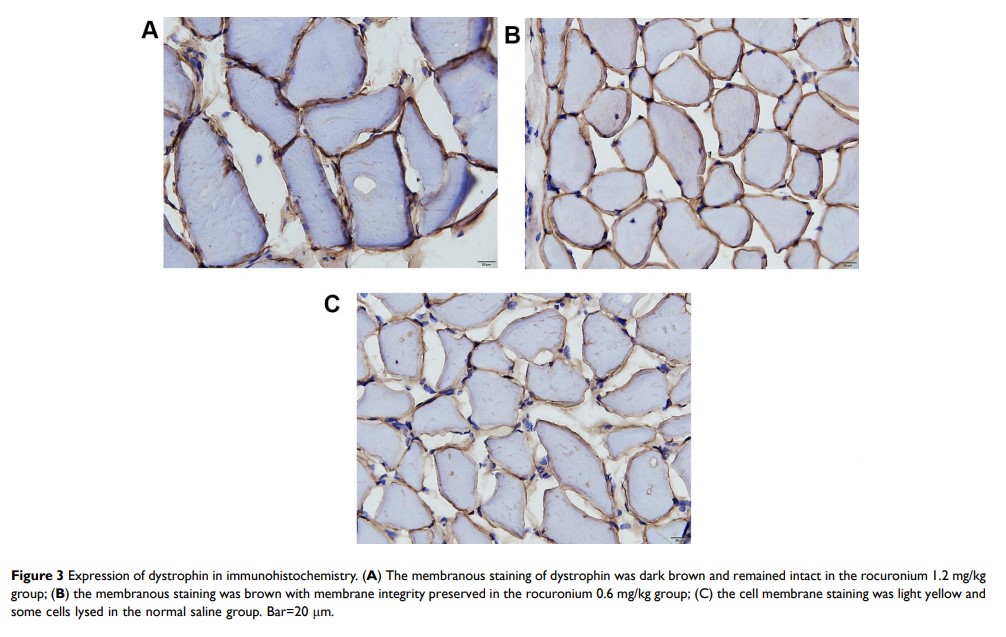
Main Results: The expression of dystrophin in the rocuronium group was higher than that in group S after ischemia (P < 0.05). The concentration of MDA in the rocuronium 1.2 mg/kg group was lower at 30 min after reperfusion (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in nNOS among groups at each time point (P > 0.05). The change of thigh girth was the smallest in the rocuronium 1.2 mg/kg group after operation (P < 0.05). The leaving bed time was significantly earlier after operation in the rocuronium group than that in group S (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Rocuronium can protect skeletal muscle from ischemia-reperfusion injury induced by tourniquet. The mechanism may be related to the fact that rocuronium can reduce the loss of dystrophin in skeletal muscle and have the effects of anti-oxidation and anti-stress.
Trial Registration: The study was registered at http://www.chictr.org.cn (ChiCTR1800019221, registered on 2018– 10-31).
Keywords: ischemia-reperfusion injury, rocuronium, dystrophin, TKA