108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

胃癌中的 15-PGDH 表达:潜在的抗肿瘤免疫作用
Authors Li Y, Li J, Dong J, Zhang L, Liu D, He J, She Y, Ma C, Liu Y
Received 12 January 2020
Accepted for publication 30 July 2020
Published 19 August 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 7419—7426
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S245726
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Introduction: Host immunity plays a vital role in tumorigenesis, including in tumor invasion and metastasis. However, the precise underlying mechanism remains to be explored. The enzyme 15-PGDH, which plays a key role in prostaglandin degradation, is a critical inflammatory mediator in gastric cancer (GC) tumorigenesis.
Materials and Methods: Immunohistochemistry was performed to determine 15-PGDH expression in GC and the corresponding adjacent non-neoplastic tissues (n=92).
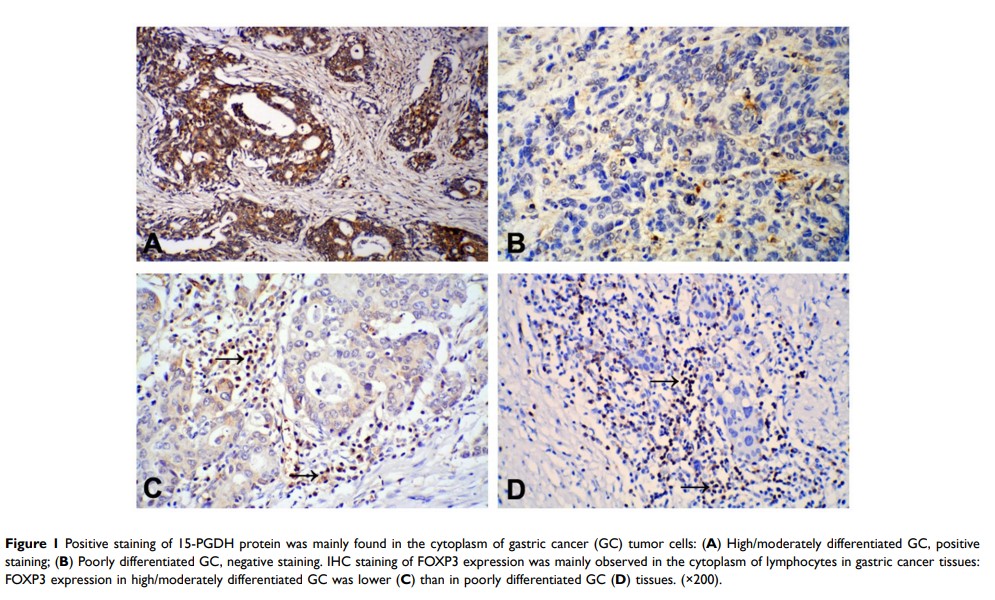
Results: The expression of 15-PGDH in GC tissues was significantly lower than that in paracancerous tissues (P < 0.001) and found to correspond inversely with GC differentiation (P= 0.043) and lymph node metastasis (P= 0.046). In contrast, FOXP3 expression was increased in poorly differentiated GC tissues (P= 0.001). Kaplan–Meier analysis revealed that GC patients with low expression of 15-PGDH (Log rank test, P= 0.007) and high expression of FOXP3 (Log rank test, P= 0.009) had shorter overall survival (OS) than those with high 15-PGDH and low FOXP3 expression. OS was also correlated with pathological tumor-node-metastasis stage (Log rank test, P= 0.014). Furthermore, using Cox proportional hazard regression, 15-PGDH expression [hazard ratio (HR): 0.605 (0.440– 0.833); P= 0.002] was identified as an independent factor for OS.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that 15-PGDH may contribute to anti-tumor immunity by regulating FOXP3+ Treg cells. The findings are useful for the identification of therapeutic targets for the management of GC.
Keywords: gastric cancer, 15-PGDH, immunosuppression, FOXP3, Tregs