108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA H19 通过上调 cAMP 反应元件结合蛋白中的周期蛋白依赖性激酶 5 介导的磷酸化引起神经性疼痛
Authors Li K, Jiao Y, Ren X, You D, Cao R
Received 27 November 2019
Accepted for publication 17 July 2020
Published 20 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2113—2124
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S240273
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Michael Schatman
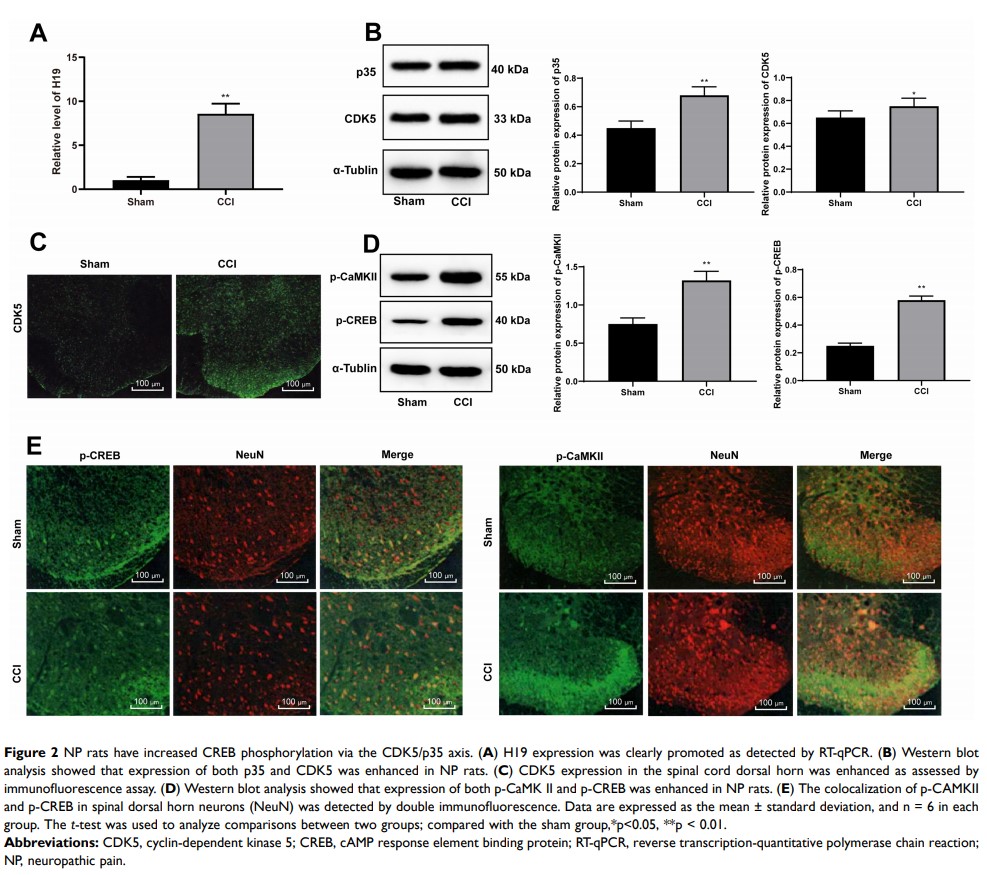
Objective: Neuropathic pain (NP) is a debilitating condition caused by nervous system injury and chronic diseases. LncRNA H19 is upregulated in many human diseases, including NP. Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) aggressively worsens inflammatory action and nerve damage to cause severe NP. Phosphorylated cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) is detrimental to nerves and promotes NP progression. Herein, aim of our study was to assess the mechanism of lncRNA H19.
Methods: The NP rat model was established using chronic constriction injury (CCI). Paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) tests and paw withdrawal latency (PWL) tests were performed. Then, small interfering (si)RNA against H19 was intrathecally injected into rats to suppress H19 expression. Schwann cells were isolated from NP rats and transfected with siRNA-H19 or a lentivirus (LV)-based vector expressing H19. Inflammatory factors and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) were detected. Western blot analysis was conducted to detect CDK5/p35 and p-CREB expression. Finally, H19, CDK5 and CREB phosphorylation were tested with the combination of the CDK5 inhibitor roscovitine and transfection of LV-H19 and siRNA-H19. Finally, we investigated the binding relationships between H19 and miR-196a-5p and between miR-196a-5p and CDK5 and detected the mRNA expression of miR-196a-5p and CDK5 in rats with H19 knockdown and in Schwann cells with H19 knockdown.
Results: Highly expressed H19, CDK5/p-35 and p-CREB were observed in NP rats, accompanied by obviously decreased PWT and PWL, upregulated inflammatory factors and GFAP levels, and reduced 5-HT2A and GABAB2 expression. siRNA-H19 restored NP-related indexes and downregulated CDK5/p35 and p-CREB phosphorylation. siRNA-H19, together with the CDK5 inhibitor roscovitine, reduced CDK5 and p-CREB expression in Schwann cells isolated from NP rats. Binding sites between H19 and miR-196a-5p and between miR-196a-5p and CDK5 were identified. Silencing H19 upregulated miR-196a-5p expression and downregulated CDK5 levels.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that silencing H19 inhibited NP by suppressing CDK5/p35 and p-CREB phosphorylation via the miR-196a-5p/CDK5 axis, which may provide new insight into NP treatment.
Keywords: neuropathic pain, long noncoding RNA H19, cyclin-dependent kinases 5, cAMP response element binding protein phosphorylation, roscovitine