108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

环磷酰胺特农囊下微灌注对严重眼部炎症兔子的功效
Authors Zhao L, Peng M, Lin W, Tan Q, Khan MA, Lin D
Received 19 February 2020
Accepted for publication 5 August 2020
Published 20 August 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 3407—3416
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S250541
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Georgios D. Panos
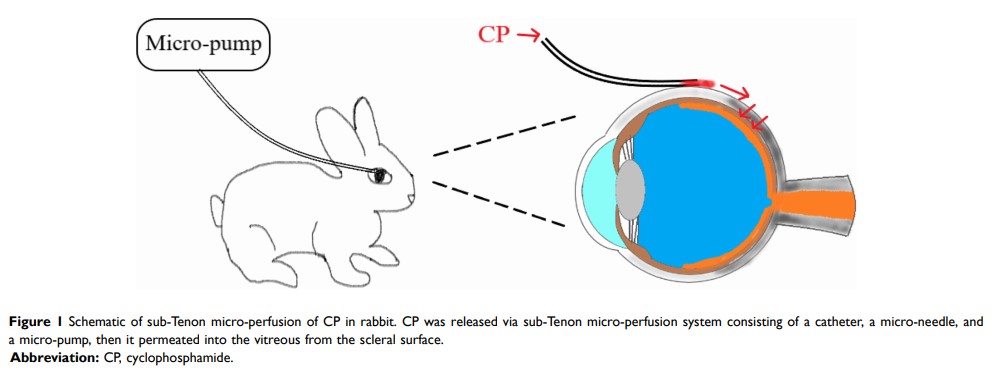
Purpose: To explore the feasibility of cyclophosphamide (CP) via a sub-Tenon micro-perfusion system (SMS) in rabbits, and assess its therapeutic efficacy in severe ocular inflammation.
Materials and Methods: Distribution and pharmacokinetics of CP were evaluated in vivo, and the concentrations of CP in plasma, vitreous humor, and retina/choroid were quantitated by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) at different time points. After induction of severe experimental uveitis, rabbits were divided into three groups (n=8 in each): the SMS group, subconjunctival injection (SI) group, and control group. Clinical inflammatory score was assessed in rabbits. Electroretinography and histopathology were performed on post-treatment day 8. Statistical analyses were performed using Mann–Whitney and Kruskal–Wallis tests. P -value less than 0.05 was considered significant.
Results: The concentrations of CP in vitreous humor and retina/choroid in the SMS group were significantly higher than that of the SI group at 3, 6, 10, and 24 hours (P < 0.01), while plasmatic CP concentrations were comparable at all time points in the SMS group and SI group (P > 0.05). The SMS group showed significantly less inflammation compared to the control group and SI group. Furthermore, the restoration of retinal structure and function were more obvious in the SMS group compared with conventional SI application.
Conclusion: Sub-Tenon micro-perfusion of CP exhibited satisfied therapeutic efficacy in rabbits with severe ocular inflammation and may provide a promising alternative for controlling ocular inflammatory disease and immune-mediated ocular diseases.
Keywords: cyclophosphamide, sub-Tenon drug delivery, ocular inflammation, treatment, rabbit