108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

大鼠气管内给药后,TiO2 纳米粒子通过 ROS 激活的 FOXO3a 信号通路在肺和肺外器官中造成 DNA 损伤
Authors Han B, Pei Z, Shi L, Wang Q, Li C, Zhang B, Su X, Zhang N, Zhou L, Zhao B, Niu Y, Zhang R
Received 30 March 2020
Accepted for publication 17 July 2020
Published 21 August 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 6279—6294
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S254969
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Introduction: Because of the increased production and application of manufactured Nano-TiO2 in the past several years, it is important to investigate its potential hazards. TiO2 is classified by IARC as a possible human carcinogen; however, the potential mechanism of carcinogenesis has not been studied clearly. The present study aimed to investigate the mechanism of DNA damage in rat lung and extra-pulmonary organs caused by TiO2 nanoparticles.
Methods: In the present study, SD rats were exposed to Nano-TiO2 by intratracheal injection at a dose of 0, 0.2, or 1 g/kg body weight. The titanium levels in tissues were detected by ICP-MS. Western blot was used to detect the protein expression levels. The DNA damage and oxidative stress were detected by comet assay and ROS, MDA, SOD , and GSH-Px levels, respectively.
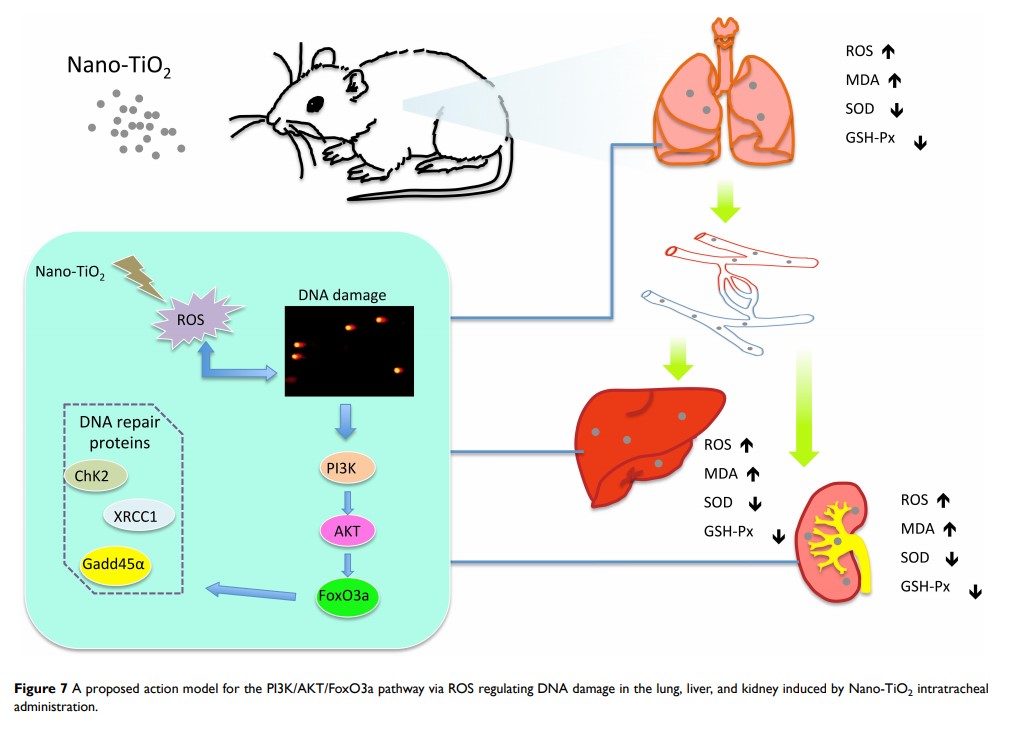
Results: The titanium levels of the 1 g/kg group on day-3 and day-7 were significantly increased in liver and kidney as well as significantly decreased in lung compared to day-1. ROS and MDA levels were statistically increased, whereas SOD and GSH-Px levels were statistically decreased in tissues of rats in dose-dependent manners after Nano-TiO2 treatment. PI3K , p-AKT /AKT , and p-FOXO3a /FOXO3a in lung, liver, and kidney activated in dose-dependent manners. The levels of DNA damage in liver, kidney, and lung in each Nano-TiO2 treatment group were significantly increased and could not recover within 7 days. GADD45α , ChK2 , and XRCC1 in liver, kidney, and lung of rats exposed to Nano-TiO2 statistically increased, which triggered DNA repair.
Conclusion: This work demonstrated that Ti could deposit in lung and enter extra-pulmonary organs of rats and cause oxidative stress, then trigger DNA damage through activating the PI3K-AKT-FOXO3a pathway and then promoting GADD45α , ChK2 , and XRCC1 to process the DNA repair.
Keywords: Nano-TiO2, DNA damage, PI3K/AKT/FOXO3a signaling pathway, DNA repair, GADD45α/ChK2/XRCC1 signaling pathway