108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

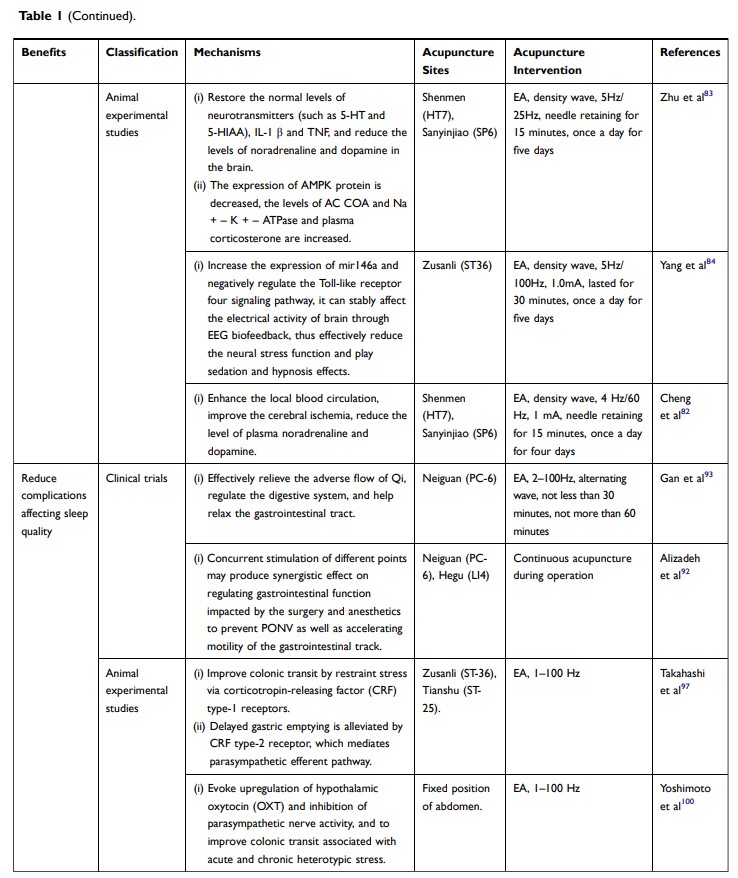
电针:改善全身麻醉手术后睡眠质量的新方法
Authors Luo M, Song B, Zhu J
Received 3 May 2020
Accepted for publication 4 August 2020
Published 21 August 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 583—592
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NSS.S261043
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sutapa Mukherjee
Abstract: General anesthesia produces a state of drug-induced unconsciousness that is controlled by the extent and duration of administered agents. Whether inhalation or intravenous in formulation, such agents may interfere with normal sleep–wake cycles, impairing postoperative sleep quality and creating complications. Electroacupuncture is a new approach widely applied in clinical practice during recent years. This particular technology helps regulate neurotransmitter concentrations in the brain, lowering norepinephrine and dopamine levels to improve sleep quality. It also alleviates surgical pain that degrades postoperative sleep quality after general anesthesia by downregulating immune activity (SP, NK-1, and COX-1) and upregulating serotonin receptor (5-HT1AR, 5-HT2AR) and endocannabinoid expression levels. However, large-scale, multicenter studies are still needed to determine the optimal duration, frequency, and timing of electroacupuncture for such use.
Keywords: general anesthesia, sleep quality, acupoints, electroacupuncture