108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

纳米颗粒性质对药物口服生物利用度的影响
Authors Wang Y, Pi C, Feng X, Hou Y, Zhao L, Wei Y
Received 7 April 2020
Accepted for publication 13 July 2020
Published 24 August 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 6295—6310
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S257269
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
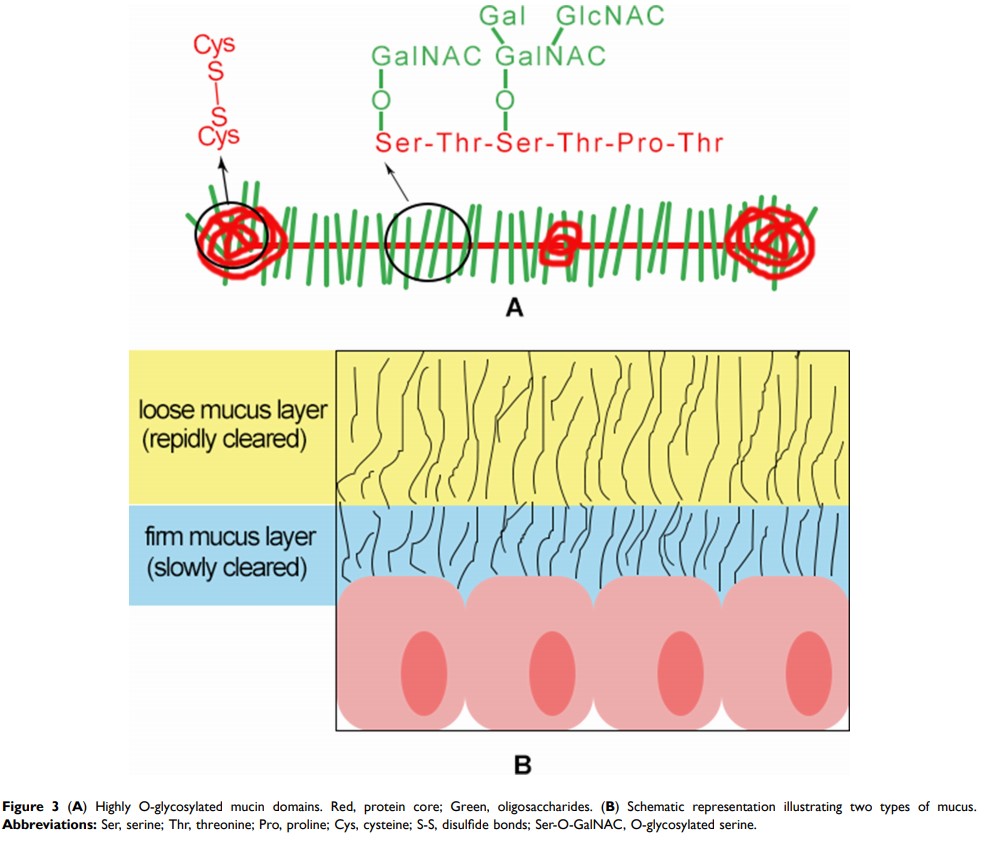
Abstract: Oral administration has been the most common therapeutic regimen in various diseases because of its high safety, convenience, lower costs, and high compliance of patients. However, susceptible in hostile gastrointestinal (GI) environment, many drugs show poor permeability across GI tract mucus and intestinal epithelium with poor oral absorption and limited therapeutic efficacy. In recent years, nanoparticulate drug delivery systems (NDDS) have become a hot research spot because of their unique advantages including protecting drug from premature degrading and interacting with the physiological environment, increasing intracellular penetration, and enhancing drug absorption. However, a slight change in physicochemistry of nanoparticles can significantly impact their interaction with biological pathways and alter the oral bioavailability of drugs. Hence, this review focuses on the factors affecting oral bioavailability from two aspects. On the one hand, the factors are the biochemical and physiological barriers in oral drugs delivery. On the other hand, the factors are the nanoparticle properties including size, surface properties, and shape of nanoparticles.
Keywords: oral bioavailability, nanoparticle properties, size, shape, surface properties