108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

左炔诺孕酮通过 lncRNA H19/miR-17/TLR4 信号通路改善子宫腺肌病
Authors Liang N, Zhang W, Wang H, Shi W, Wang L, Ma L
Received 2 February 2020
Accepted for publication 26 June 2020
Published 24 August 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 3449—3460
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S248095
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianbo Sun
Purpose: To explore the mechanism of levonorgestrel (LNG)-ameliorating adenomyosis through long non-coding RNA H19 (lncRNA H19)/miR-17/Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) pathway.
Patients and Methods: A total of 71 cases of adenomyosis and 54 cases of normal endometrium were sampled. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) was employed to quantify lncRNA H19, miR-17, and TLR4 mRNA, while Western blot (WB) was used to quantify TLR4 protein. Effects of LNG on normal endometrial stromal cells (ESCs) were evaluated. Suppression/over-expression vectors of lncRNA H19, miR-17, and TLR4 were constructed to observe their effects on ESCs.
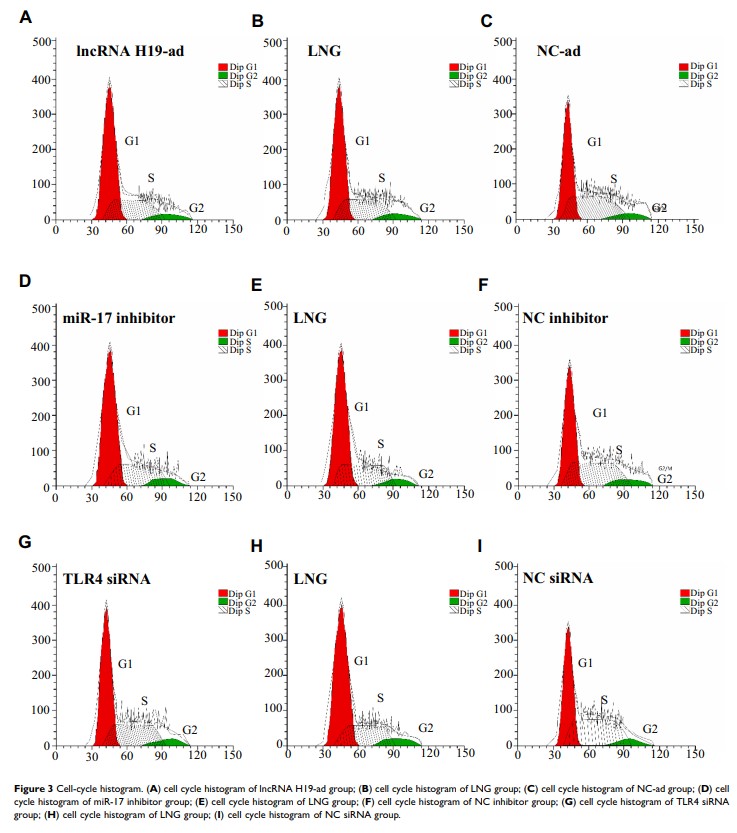
Results: MiR-17 and TLR4 mRNA were up-regulated and lncRNA H19 was down-regulated in adenomyosis. After LNG treatment, lncRNA H19 was up-regulated while miR-17 and TLR4 were down-regulated. LNG, up-regulation of lncRNA H19, and down-regulation of miR-17 and TLR4 portend increased apoptosis, G1-arrested cells, as well as inhibited inflammation. Dual-luciferase reporter (DLR) assay conformed the targeting relation of lncRNA H19/miR-17/TLR4 pathway.
Conclusion: LNG ameliorates adenomyosis via lncRNA H19/miR-17/TLR4 pathway.
Keywords: adenomyosis, levonorgestrel, lncRNA H19/miR-17/TLR4 pathway