108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

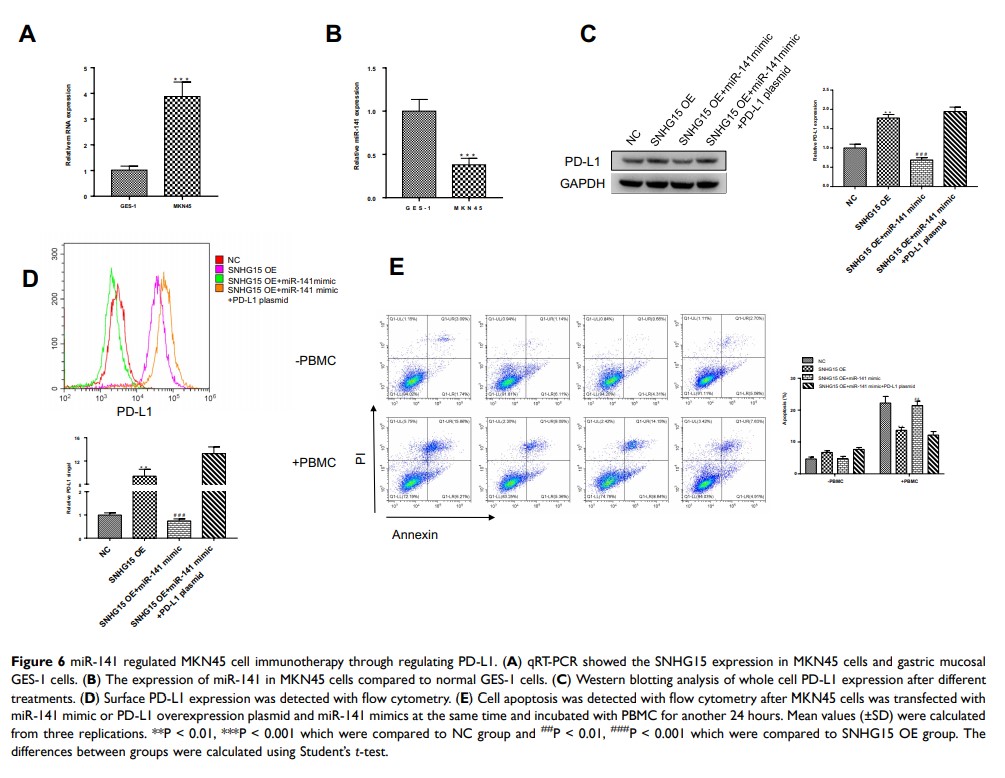
LncRNA SNHG15 通过靶向 miR141/PD-L1 促进胃癌的免疫逃逸
Authors Dang S, Malik A, Chen J, Qu J, Yin K, Cui L, Gu M
Received 15 April 2020
Accepted for publication 1 August 2020
Published 24 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 8547—8556
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S251625
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Introduction: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been demonstrated to participate in many biological processes and severs as important regulators during the progression of gastric cancer.
Methods: Here, we introduced human lncRNA SNHG15 which was highly expressed in gastric cancer and cells. Interestingly, the expression of SNHG15 was correlated with programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1), which promotes the resistance of gastric cancer cells to immune responses. Meanwhile, SNHG15 downregulation suppressed the expression of PD-L1 and resistance of immune responses.
Results: Further, our results suggested that SNHG15 acted as a competing endogenous RNA (CeRNA) to sponge miR-141, which was downregulated in gastric cancers and negatively correlated to PD-L1.
Conclusion: Our results suggested that SNHG15 improved the expression of PD-L1 by inhibiting miR-141, which in turn promoted the resistance of stomach cancer cells to the immune responses.
Keywords: lncRNA SNHG15, gastric cancer, PD-L1, immuno-escape, miR-141