108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

WAVE2 在结直肠癌肝转移中增强了肝星状细胞的活性
Authors Tan F, He D, Hu K, Wang D, Zhang S, Li J, Wang Z, Tao Y
Received 29 April 2020
Accepted for publication 5 August 2020
Published 24 August 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 7671—7680
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S259125
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
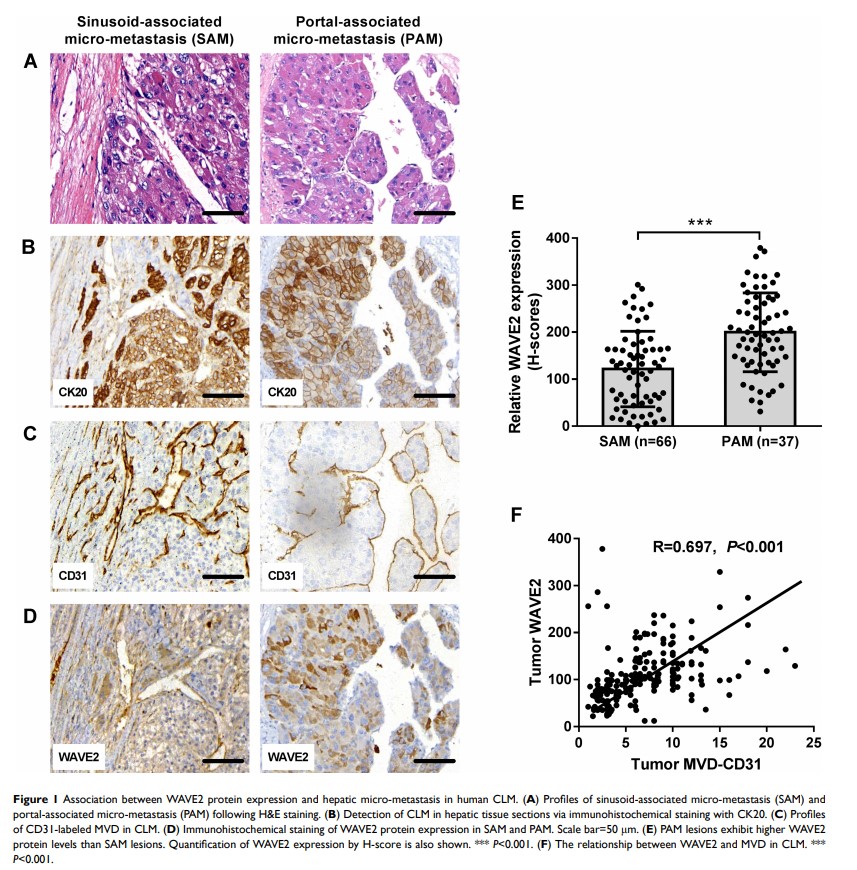
Background: Cancer cell migration, tumor angiogenesis, and activated hepatic stellate cells (a-HSCs) promote the development of colorectal liver metastases (CLM). Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein family verprolin-homologous protein 2 (WAVE2) has been associated with CLM, although the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear.
Methods: In the current study, we evaluated the relationship between WAVE2 and CLM in 103 CLM patients who underwent liver resection. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining was performed to determine the association between WAVE2 protein expression and hepatic micro-metastasis in human CLM tissues. WAVE2 knockout was performed in hepatic stellate cells (HSC) to explore the function and signaling pathways of WAVE2 in colorectal cancer progression.
Results: Significantly higher levels of WAVE2 were detected in portal-associated relative to sinusoid-associated micro-metastasis. A strong correlation was identified between WAVE2 levels and microvessel density (MVD) in hepatic metastasis. Similarly, expression of WAVE2 was closely associated with activation of HSCs. Mechanistically, WAVE2 regulated the progression of human CLM acts by regulating the growth factor β (TGF-β) and Hippo pathways via effector yes-associated protein (YAP1).
Conclusion: Overall, our results demonstrated that WAVE2 participates in CLM tumor microenvironment, and can be a potential latent therapeutic target for CLM.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, hepatic stellate cells, liver metastasis, WAVE2