108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

lncRNA PART1 通过直接靶向 miR-4516 促进乳腺癌细胞进展
Authors Wang Z, Xu R
Received 9 March 2020
Accepted for publication 7 July 2020
Published 24 August 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 7753—7760
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S249296
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Seema Singh
Introduction: Breast cancer is a serious threat to human health. It is meaningful to study the pathogenesis of breast cancer. lncRNAs have been found to play vital roles in numerous biological processes including development, immunology and cancer.
Methods: qRT-PCR was performed to examine the expressions of PART1 and miR-4516. CCK-8 assay, colony formation assay and transwell assay were used to examine the progression of breast cancer cells.
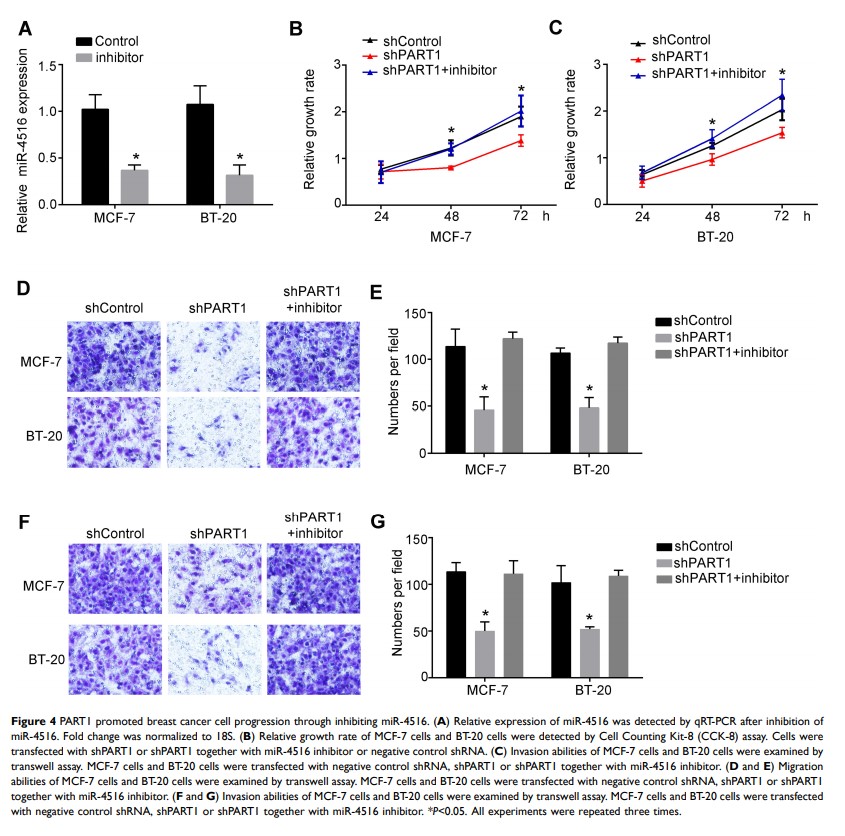
Results: In this study, we showed that lncRNA PART1 was highly expressed in breast cancer cells. Knockdown of PART1 induced decreased proliferation, invasion and migration of breast cancer cells. Moreover, we found that PART1 can bind to miR-4516 directly. We also found that inhibition of miR-4516 could rescue the decreased proliferation, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells induced by knockdown of PART1.
Discussion: lncRNA PART1 and miR-4516 were proven to be involved in the progression of many cancers. However, the roles of lncRNA PART1 and miR-4516 in the regulation of breast cancer remain unknown. Here, we demonstrated that PART1 can bind to miR-4516 to decrease the expression of miR-4516 and promote the development of breast cancer.
Keywords: PART1, miR-4516, breast cancer, proliferation, migration, invasion