108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MALAT1 通过调节 miR-515-5p/EEF2 轴来促进非小细胞肺癌的细胞致瘤性
Authors Rong F, Liu L, Zou C, Zeng J, Xu Y
Received 15 December 2019
Accepted for publication 6 August 2020
Published 24 August 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 7691—7701
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S242425
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: Previous studies suggested long noncoding RNA metastasis associated with lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (lncRNA MALAT1) acted as a tumor promoter to promote cell carcinogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). MALAT1 was found to exist in serum exosomes of several cancers. However, the role of exosomal-derived MALAT1 in NSCLC remains poorly understood.
Materials and Methods: Exosomes were isolated using the ExoQuick precipitation kit. Western blot was used to detect the protein expression of CD3, CD63, apoptosis- and metastasis-related protein. The expression of MALAT1, microRNA (miR)-515-5p and eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (EEF2 ) mRNA was detected using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Cell viability, apoptosis, or invasion were measured using 3-(4, 5)-dimethylthiahiazo (-z-y1)-3, 5-di-phenytetrazoliumromide (MTT) assay, flow cytometry or transwell assay, respectively. The interaction between miR-515-5p and MALAT1 or EEF2 was confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter assay. In vivo experiments were conducted through the murine xenograft model.
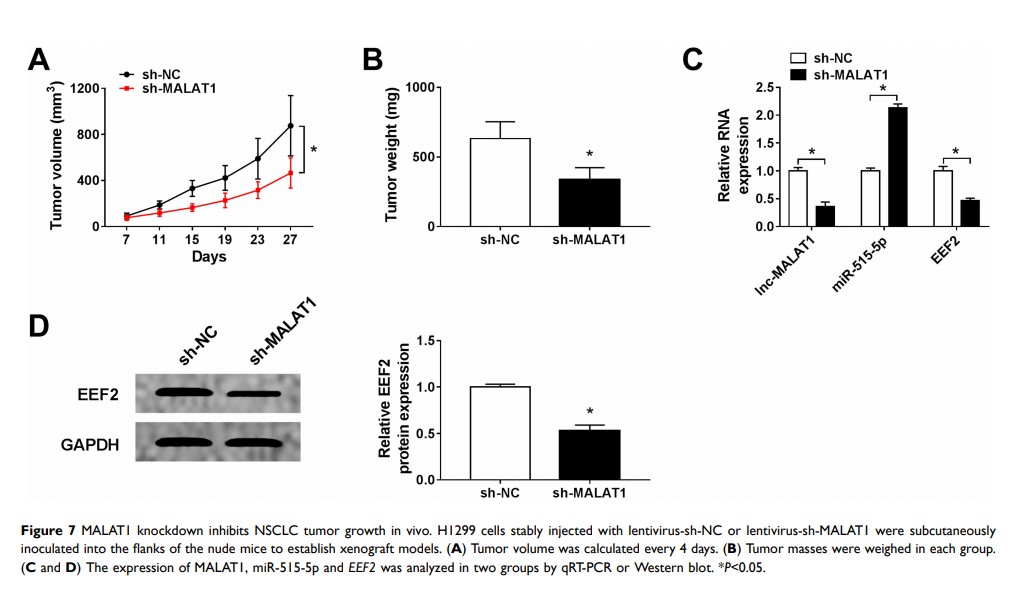
Results: MALAT1 was highly expressed in serum and cell exosomes from NSCLC patients. MALAT1 knockdown repressed cell proliferation, invasion and induced cell apoptosis in vitro as well as inhibited tumor growth in vivo in NSCLC. Subsequently, we confirmed that MALAT1 was a sponge of miR-515-5p, and EEF2 was a target of miR-515-5p. Furthermore, MALAT1 served as a sponge of miR-515-5p to regulate EEF2 expression in NSCLC cells. More importantly, MALAT1 deletion performed anti-tumor effects by interacting with miR-515-5p/EEF2 axis in vitro and in vivo in NSCLC.
Conclusion: MALAT1 knockdown repressed NSCLC tumorigenicity by inhibiting cell proliferation, invasion and promoting apoptosis through regulating miR-515-5p/EEF2 , besides, MALAT1 was highly enriched in exosomes of NSCLC, suggesting a possible molecular-targeted therapy for NSCLC patients.
Keywords: MALAT1, miR-515-5p, EEF2 , NSCLC, tumorigenicity, exosomes