108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国东南部 2 型糖尿病患者的胰岛素起始治疗延迟:一项回顾性现实世界研究
Authors Chen P, Ma X, Chen H, Wang K, Zhou L
Received 1 April 2020
Accepted for publication 10 July 2020
Published 25 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3059—3068
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S256381
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonio Brunetti
Purpose: To describe the extent of delays in insulin initiation, analyze its impact on glycemic control, and explore factors influencing delayed insulin initiation among Chinese type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients.
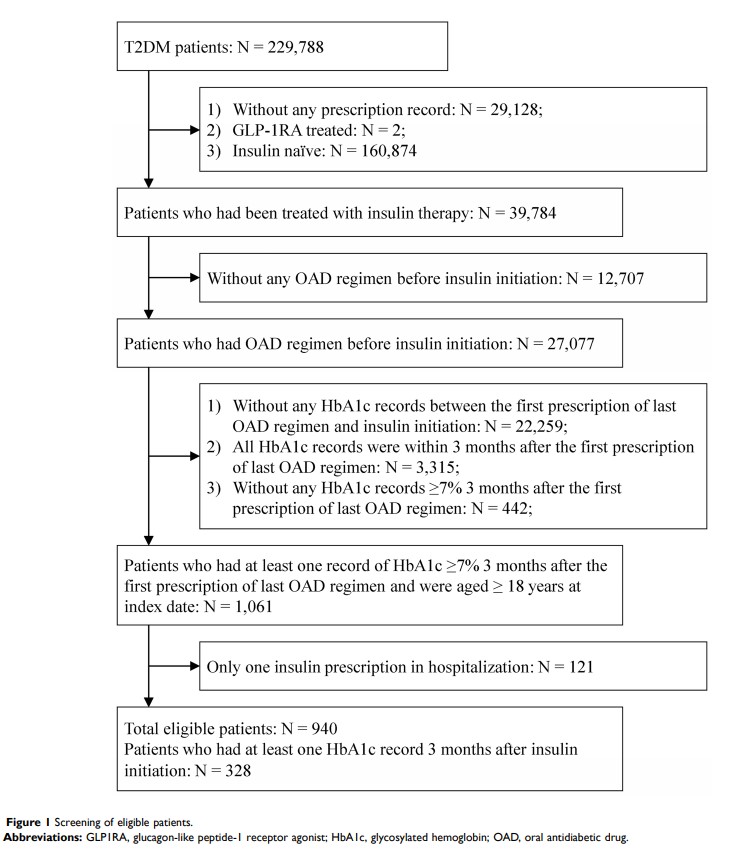
Methods: A real-world, retrospective cohort study with regional electronic health records from Fuzhou, southeast China was conducted among T2DM patients. Adult patients uncontrolled with oral antidiabetic drugs (OADs; HbA1c ≥ 7%) and initiated on insulin treatment were included. Time to insulin initiation was described. After propensity-score matching, Wilcoxon rank-sum test and chi-square test were used to compare follow-up HbA1c (first HbA1c 3 months after insulin initiation) between timely (initiated insulin within 6 months after OAD failure) and delayed (initiated after 6 months) insulin-initiation groups. Sensitivity analysis was also performed by linear and logistic regression. Factors associated with delayed insulin initiation were explored using logistic regression.
Results: A total of 940 patients were included, with mean±SD age 66.3± 11.9 years. In sum, 328 had HbA1c recorded 3 months after insulin initiation. After propensity-score matching (1:1 matching), 184 patients were included for further analysis. Median follow-up HbA1c was lower in the timely-initiation group than the delayed-initiation group (7.25% vs 8.25%, P =0.009). Patients in the timely initiation group also had higher odds of achieving HbA1c < 7% (OR=3.15, P =0.001). Results were confirmed by logistic regression. Hypertension, coronary artery disease, baseline HbA1c, and hospital level at insulin initiation were associated with delays in insulin initiation.
Conclusion: Timely insulin initiation after OAD failure is associated with better glycemic control.
Keywords: type 2 diabetes mellitus, therapeutic inertia, delayed insulin initiation, glycemic control, HbA1c