108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

采用尿液代谢组学确定中风后抑郁症中年患者的潜在代谢物标记
Authors Xie J, Han Y, Hong Y, Li W, Pei Q, Zhou X, Zhang B, Wang Y
Received 14 July 2020
Accepted for publication 10 August 2020
Published 25 August 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 2017—2024
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S271990
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yuping Ning
Background: Post-stroke depression (PSD) is one of the most common complications in stroke survivors. But, there are still no objective methods to diagnose PSD. This study aims to identify potential biomarkers for diagnosing PSD in middle-aged stroke survivors.
Methods: Middle-aged subjects aged 30 to 59 years (92 PSD patients and 89 stroke survivors without depression) were included in this study. Urinary metabolites were detected by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Differential urinary metabolites and potential biomarkers were screened by applying statistical analysis.
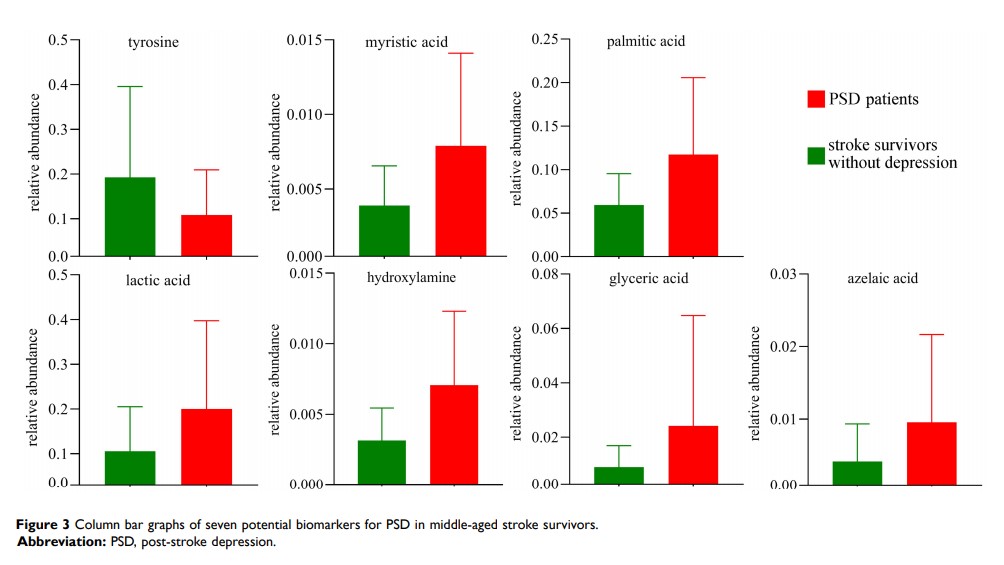
Results: The different urinary metabolic phenotypes between PSD patients and stroke survivors without depression were identified. A total of 12 differential urinary metabolites were accurately identified by using orthogonal partial least-squares-discriminant analysis. After analyzing those 12 differential urinary metabolites by step-wise logistic regression analysis, only seven metabolites (palmitic acid, hydroxylamine, myristic acid, glyceric acid, lactic acid, tyrosine and azelaic acid) were finally selected as potential biomarkers for diagnosing PSD in middle-aged stroke survivors. A panel consisting of these potential biomarkers could effectively diagnose middle-aged PSD patients.
Conclusion: Urinary metabolic profiles were different between middle-aged PSD patients and stroke survivors without depression. Our results would be helpful in future for developing an objective method to diagnose PSD in middle-aged stroke survivors.
Keywords: post-stroke depression, biomarkers, metabolites