108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA KCNQ1OT1 通过充当 miR-27b-3p 的分子海绵并随后增加 ATF2 表达来促进脊索瘤的多药耐药性
Authors Li L, Lv G, Wang B, Ma H
Received 20 February 2020
Accepted for publication 13 April 2020
Published 25 August 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 7847—7853
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S250611
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Harikrishna Nakshatri
Background: Chordoma, a rare bone tumor, occurs most commonly at the sacrococcygeal and skull base region. To date, chemotherapy is used to treat patients with advanced-stage chordoma. However, multidrug resistance (MDR) greatly hinders the effect of chemotherapy in chordoma. Here, we studied the correlation between KCNQ1OT1 and chemotherapy resistance.
Methods: RT-PCR assay was used to examine KCNQ1OT1, miR-27b-3p, and ATF2 mRNA expression. CCK8 assay was exercised to detect IC50 values of cisplatin in chordoma cells. ATF2 protein expression was detected by Western blot.
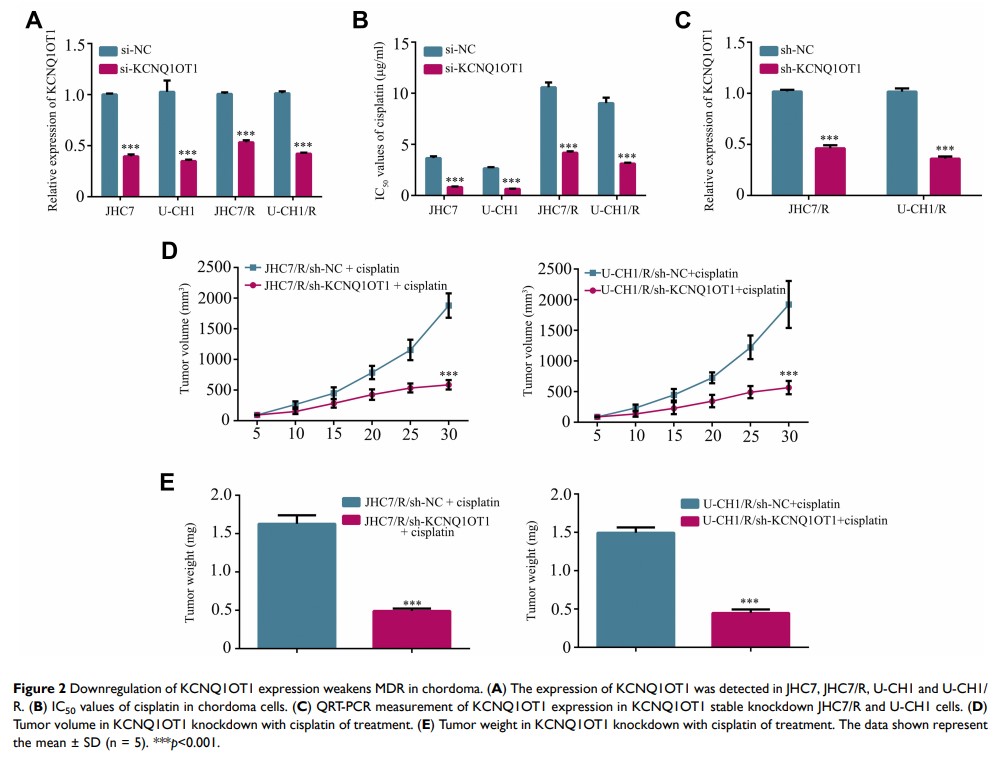
Results: KCNQ1OT1 was increased in chemotherapy-resistant patients and cisplatin-resistant cells, and downregulation of KCNQ1OT1 expression weakened MDR in chordoma. In addition, KCNQ1OT1 promoted MDR in chordoma by sponging miR-27b-3p and subsequently increasing ATF2 expression.
Conclusion: KCNQ1OT1 is proved to be strikingly raised in the chemotherapy-resistant group and to promote MDR in chordoma. Our findings demonstrated the role of the KCNQ1OT1/miR-27b-3p/ATF2 axis in MDR of chordoma, which provides new insight into the molecular mechanism of chordoma MDR, and may determine the effect of therapy after receiving chemotherapy by detecting the expression of KCNQ1OT1 in serum.
Keywords: KCNQ1OT1, MDR, miR-27b-3p, ATF2, chordoma