108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CPA4 通过刺激 PI3K-AKT-mTOR 信号传导促进胰腺癌的 EMT
Authors Shao Q, Zhang Z, Cao R, Zang H, Pei W, Sun T
Received 21 April 2020
Accepted for publication 30 July 2020
Published 25 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 8567—8580
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S257057
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
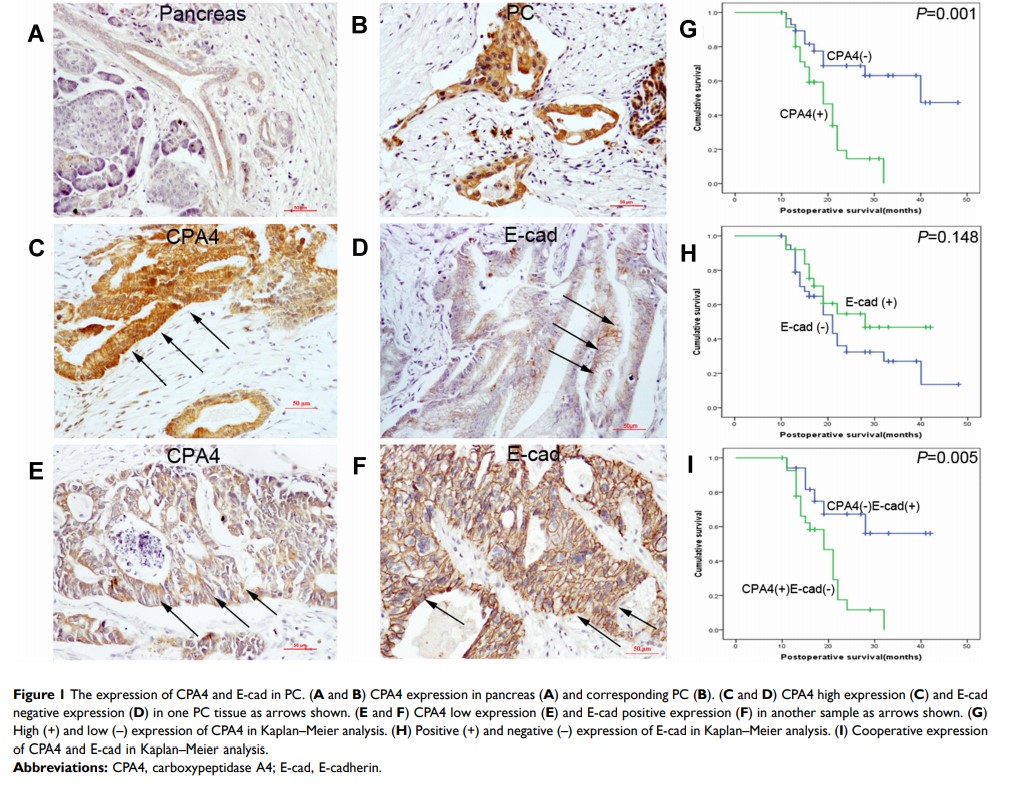
Background: Carboxypeptidase A4 (CPA4), as a novel tumor biomarker, is prevalently observed in various cancers. However, the potential role of CPA4 in pancreatic cancer (PC), to our knowledge, has not been fully clarified.
Materials and Methods: We systematically explored the detailed function of CPA4 in epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) stimulated PC in human clinical samples and in vitro.
Results: CPA4 was overexpressed in clinical PC samples that was positively related with tumor size (P =0.026), T stage (P =0.011), lymph-node metastasis (P =0.026) and a worse prognosis for PC patients (P =0.001). Interestingly, CPA4 was inversely correlated with E-cadherin (r=− 0.372, P =0.003) in clinical samples and PC cell lines which cooperatively contributed to a worse prognosis (P =0.005) for PC patients. CPA4 overexpression enhanced EMT in AsPC-1 and Capan-2 cells, which promoted EMT-like cellular morphology and cell invasion and migration. Meanwhile, CPA4 overexpression activated EMT and PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling, following with the downregulation of E-cadherin and β-catenin, and the upregulation of N-cadherin, vimentin, p-PI3K (Tyr458), p-AKT (Ser473) and p-mTOR (Ser2448). However, PI3K inhibitor LY294002 reversed CPA4 overexpression-stimulated EMT in vitro. Moreover, CPA4 was co-immunoprecipitated with AKT in two PC cells with CPA4 high expression. Conversely, CPA4 silencing inhibited EMT in PANC-1 cells. CPA4 overexpression or silencing promoted or inhibited cell proliferation and drug resistance in Capan-2 and PANC-1 cells via regulating Bcl2/Bax and cleaved-caspase3 signaling. However, LY294002 reversed CPA4 overexpression-stimulated cell proliferation and drug resistance in vitro in Bcl2/Bax and caspase3-dependent apoptosis.
Conclusion: CPA4 overexpression contributes to aggressive clinical stage of PC patients and promotes EMT in vitro via activation of PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling.
Keywords: CPA4, EMT, pancreatic cancer, PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling