108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

临床分期 IA(根据肿瘤位置)非小细胞肺癌的淋巴结转移模式
Authors Meng S, Liu G, Wang S, Yang F, Wang J
Received 19 May 2020
Accepted for publication 30 July 2020
Published 26 August 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 7875—7880
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S262623
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to investigate lymph node involvement pattern in clinical stage IA non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Patients and Methods: Clinical stage ⅠA NSCLC patients who underwent lobectomy and lymph node resection were included in this retrospective study. Mediastinal lymph node involvement was distinguished by different lobes and tumor size.
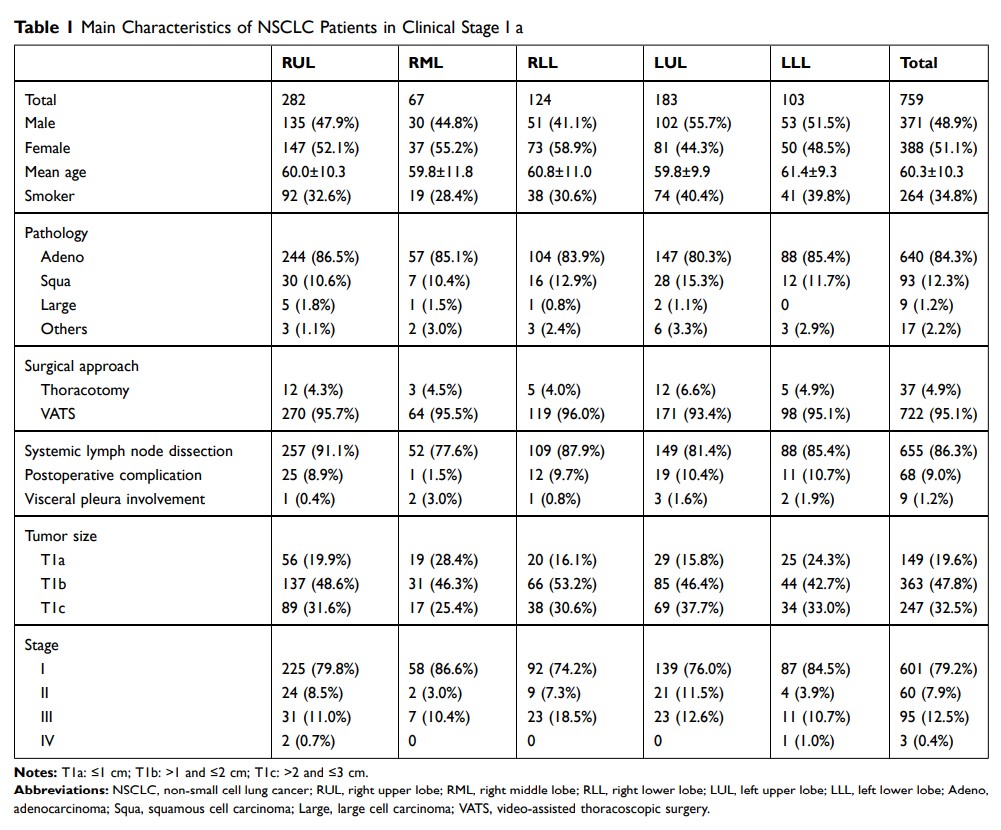
Results: From 2000 to 2015, a total of 759 patients were identified: 282 (37.2%) with tumors in the right upper lobe (RUL), 183 (24.1%) in the left upper lobe (LUL), 124 (16.3%) in the right lower lobe (RLL), 103 (13.6%) in the left lower lobe (LLL), and 67 (8.8%) in the right middle lobe (RML). Patients with tumor size ≤ 1 cm accounted for 19.6%, > 1 and ≤ 2 cm for 47.8%, > 2 and ≤ 3 cm for 32.5%. Patients with pN1 accounted for 8.2%, and pN2 for 12.5%. Among patients with pN2, the inferior mediastinum was involved in 9.7% of RULs and 17.4% of LULs; the superior mediastinum was involved in 52.2% of RLLs and 36.4% of LLLs. Mediastinal lymph node metastasis was found in 13.2% of patients with size > 1 and ≤ 2 cm, and 19.0% of > 2 and ≤ 3 cm. Patients with tumors ≤ 1 cm had no N2 lymph node involved.
Conclusion: Selective lymph node dissection based on tumor location is not recommended in clinical stage ⅠA NSCLC, and systemic lymph node dissection should be performed for NSCLC with size > 1 cm.
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer, clinical stage ⅠA, lymph node dissection, nodal involvement pattern