108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

S1PR2 敲除通过 NF-κB 激活促进多发性骨髓瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭
Authors Pang M, Li C, Zheng D, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhang W, Li F, Jing H
Received 5 November 2019
Accepted for publication 4 August 2020
Published 26 August 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 7857—7865
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S237330
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: The presence of circulating plasma cells (cPCs) was associated with a worse prognosis in multiple myeloma patients. However, the underlying mechanisms involved in the migration and invasion of bone marrow myeloma cells (BMMCs) to cPCs remains unclear. Here, we investigate the possible factors related to hematogenous myeloma cell dissemination and potential regulatory mechanisms.
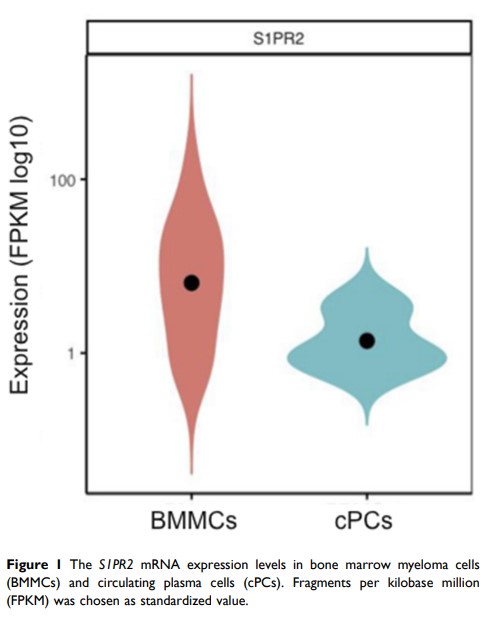
Methods: BMMCs and cPCs of five extramedullary plasmacytoma (EMP) patients were selected for single cell RNA sequencing, We found that the expression level of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 (S1RP2 ) was lower in cPCs compared with that in BMMCs. Then, we investigated the effect of S1PR2 in cell migration and invasion through pharmacologic inhibition with a S1PR2 -selective antagonist JTE-013 or knockdown of S1PR2 expression in MM cell line U266.
Results: The results showed that S1PR2 inhibition with JTE-013 or S1PR2 -shRNA significantly promoted cell migration and invasion in U266 cells. We measured the expression of invasion-related proteins by Western blot and found that knockdown of S1PR2 could reduce MMP-9 expression in U266 cells. Furthermore, we found NF-κB pathway may mediate the inhibition effects of S1PR2 on cell migration and invasion in MM cells.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrated that S1PR2 downregulation may contribute to the initial extramedullary translocation by promoting cell migration and invasion through NF-κB pathway activation.
Keywords: multiple myeloma, extramedullary plasmacytoma, circulating plasma cells, NF-κB, S1PR2