108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

利拉鲁肽和胰岛素通过 Wnt 信号通路对人脂肪组织来源的干细胞的脂肪形成有相反的作用
Authors Liu H, Zhan Y, Luo G, Zou L, Li Y, Lu H
Received 19 April 2020
Accepted for publication 30 June 2020
Published 1 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3075—3087
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S253097
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Konstantinos Tziomalos
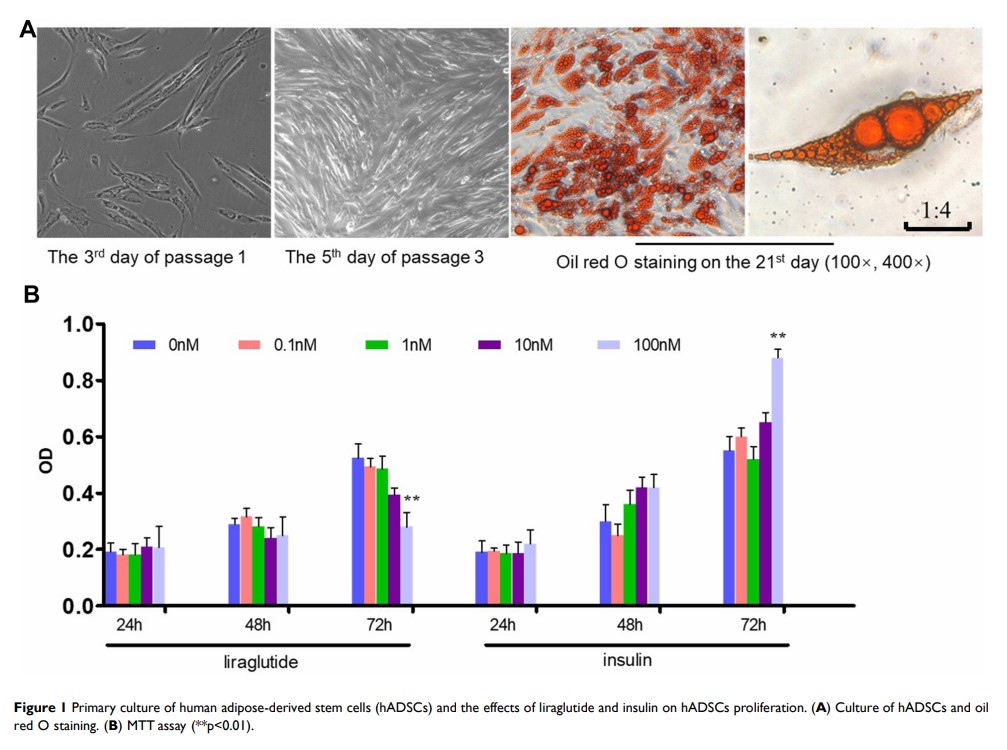
Background: Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) has been reported to have beneficial impacts on improving human’s metabolism and ameliorating insulin resistance. While insulin is another important and conventional drug in diabetes treatment, but it has an adverse effect on weight gain.
Purpose: To make sure whether GLP-1 and insulin play different roles in human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSCs).
Methods: We examined the in vitro roles and molecular mechanisms of liraglutide, a GLP-1 analogue, and human insulin on hADSCs isolated from subcutaneous adipose tissue. Different concentrations (0, 0.1, 1, 10, 100nM) of liraglutide and insulin were added to proliferation and differentiation medium of hADSCs, respectively.
Results: Liraglutide inhibits while insulin promotes the proliferation and differentiation at the concentration of 100nM. Moreover, the levels of GSK-3 increase during differentiation and liraglutide could down-regulate it when compared with insulin. We also find that the activation of phosphorylated GSK-3α and GSK-3β is involved in the differentiation roles. And classical and non-classical Wnt pathways all play roles in the differentiation, which are characterized with the up/down-regulation of the expression of adipogenesis genes such as PPAR-γ and CEBP-α.
Conclusion: Liraglutide and insulin have contrary effects on the proliferation and adipogenesis via Wnt pathway in primary cultured ADSCs. Those effects could partly explain the different roles of GLP-1 and insulin on weight gain and insulin resistance.
Keywords: liraglutide, insulin, human adipose-derived stem cells, obesity, Wnt signaling pathway