108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

大黄素通过调节 HGF 和 TGFβ-Smad 信号通路阻滞肾纤维化
Authors Yang F, Deng L, Li J, Chen M, Liu Y, Hu Y, Zhong W
Received 13 January 2020
Accepted for publication 25 July 2020
Published 3 September 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 3567—3575
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S245847
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Background: Renal fibrosis is a frequently occurring type of chronic kidney disease that can cause end-stage renal disease. It has been verified that emodin or HGF can inhibit the development of renal fibrosis. However, the antifibrotic effect of emodin in combination with HGF remains unclear.
Methods: Cell viability was detected with CCK8. Gene and protein expression in HK2 cells was detected by qRT-PCR and Western blot, respectively. Moreover, a unilateral ureteral obstruction–induced mouse model of renal fibrosis was established for investigating the antifibrotic effect of emodin in combination with HGF in vivo.
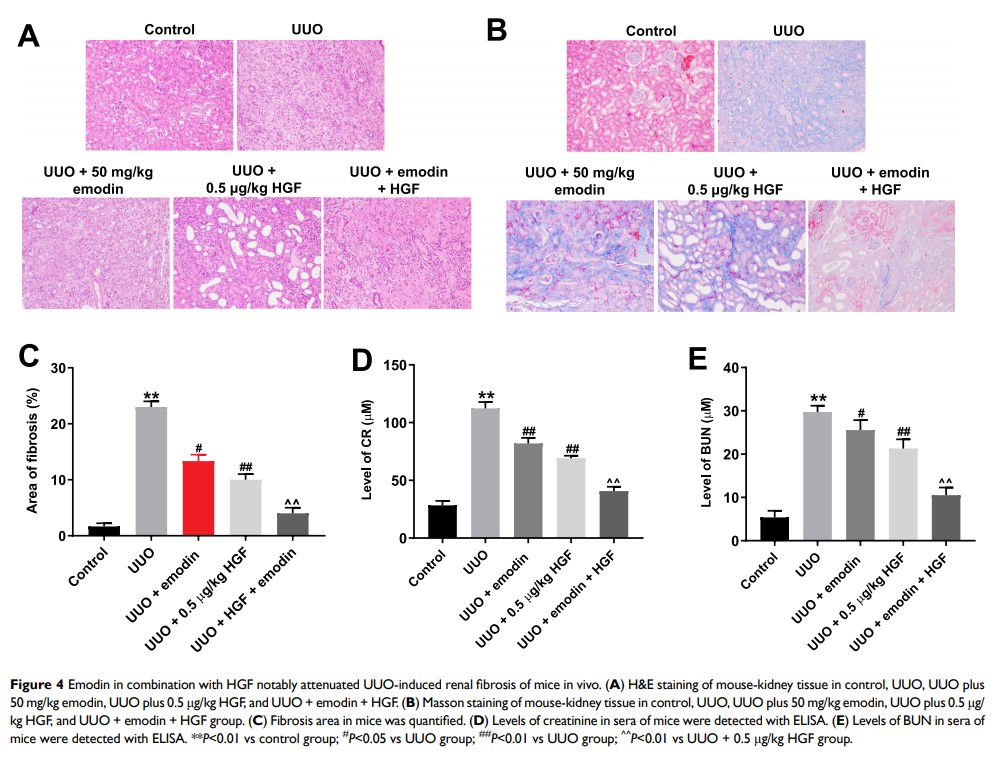
Results: HGF notably increased the expression of collagen II in TGFβ-treated HK2 cells. In addition, HGF-induced increase in collagen II expression was further enhanced by emodin. In contrast, fibronectin, αSMA and Smad2 expression in TGFβ-stimulated HK2 cells was significantly inhibited by HGF and further decreased by combination treatment (emodin plus HGF). Moreover, we found that combination treatment exhibited better antifibrotic effects compared with emodin or HGF in vivo.
Conclusion: These data demonstrated that emodin plus HGF exhibited better antifibrotic effects compared with emodin or HGF. As such, emodin in combination with HGF may serve as a new possibilty for treatment of renal fibrosis.
Keywords: fibrosis, combination, emodin, TGFβ