108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MOB1 通过靶向 PAK2 抑制大肠癌的恶性进展
Authors Liu J, Shi Z, Ma Y, Fu L, Yi M
Received 11 March 2020
Accepted for publication 3 August 2020
Published 3 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 8803—8811
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S253470
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Jianmin Xu
Objective: We aimed at studying the mechanism of MOB1 inhibiting the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer (CRC), to provide a new guidance for the early diagnosis and treatment of CRC.
Methods: MOB1 expression level in 68 pairs of CRC tissues and adjacent ones was detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis, and the associations between the expression level of MOB1 and the clinicopathological indicators as well as the prognosis of CRC patients were analyzed. After constructing CRC cell lines that stably overexpressing or silencing MOB1, the changes of cell proliferation and metastasis ability were examined by Cell Counting Kit (CCK-8) and Transwell assay. In addition, the interaction between MOB1 and PAK2 and how the these two genes affect the biological functions of CRC cell lines were investigated by luciferase assay, qRT-PCR and Western Blot experiments.
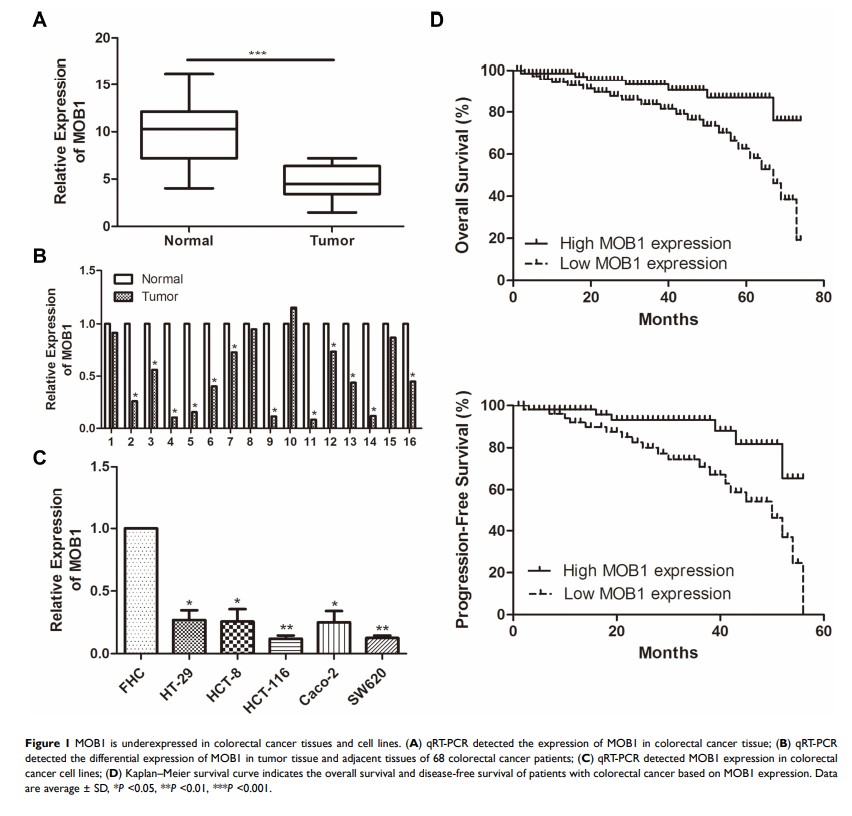
Results: Our data showed that MOB1 expression level in CRC tissues was remarkably lower than that in adjacent ones. In comparison to patients of the group of high MOB1 expression, these patients of low MOB1 expression group showed higher incidence of distant or lymph node metastasis and lower survival rate. Cell functional experiments revealed that overexpression of MOB1 markedly attenuated the proliferation and migration ability of CRC cell lines compared to the NC group; In contrast, knockdown of MOB1 enhanced the above-mentioned cell abilities compared to anti-NC group. Luciferase assay verified an interaction between MOB1 and PAK2; and Western blot analysis showed a negative correlation between the expression of the MOB1 and PAK2 protein levels in CRC tissues. Subsequently, we demonstrated that MOB1 interacted with PAK2 to regulate its expression and affected the proliferation and migration capacity of CRC cell lines in vitro.
Conclusion: In summary, the lowly expressed MOB1 in CRC tissues and cell lines may accelerate the proliferation and migration through modulating PAK2 expression.
Keywords: MOB1, PAK2, CRC, malignant progression