108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过转移 miR-613 在非小细胞肺癌中形成外泌体逆转的顺铂化学耐药性
Authors Li D, Meng D, Niu R
Received 17 March 2020
Accepted for publication 6 July 2020
Published 3 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 7961—7972
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S254310
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Harikrishna Nakshatri
Introduction: Non-small lung cancer (NSCLC) is one of the most common malignant tumors in the world. Chemoresistance is the main reason of adverse effects leading to the death of patients; thus, it is important to discover the potential target of chemotherapeutic resistance.
Methods: The expression of differentially expressed miRNA was detected in BEAS-2B, A549 and A549/cisplatin (DDP) by qRT-PCR. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and exosome biomarkers were used to validate the extracted exosome. Cells incubated with miR-613 enriched exosomes were used to detect the function of exo-miR-613 in vitro. Then, exo-miR-613 was injected to mice treated with DDP to investigate the function role of exo-miR-613 in vivo.
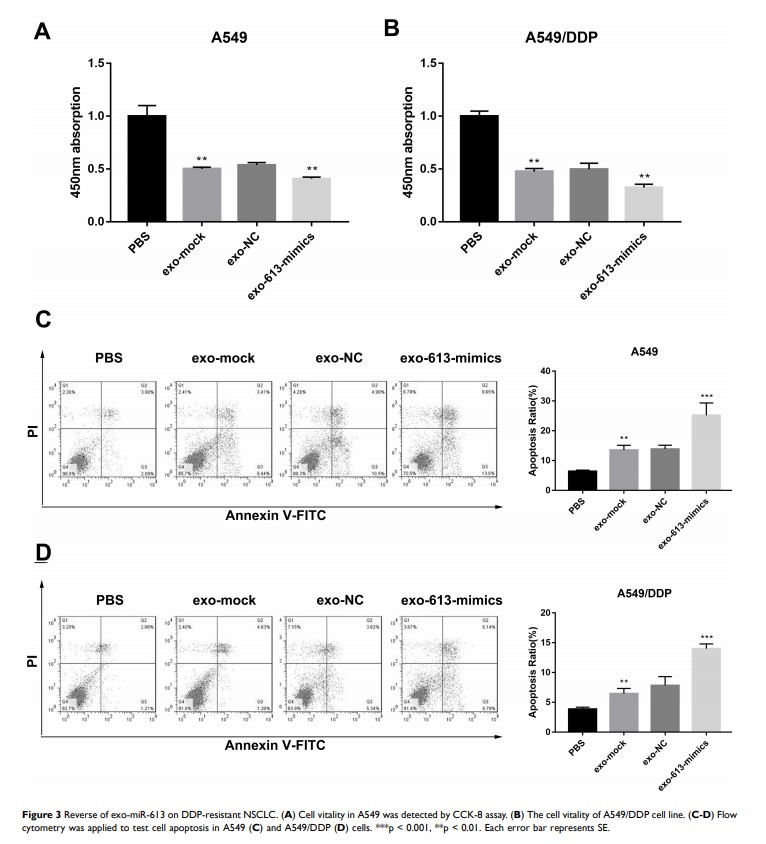
Results: Comparing to BEAS-2B, the expression of miR-613 inA549 was significantly reduced, which was more obvious in A549/DDP. After incubated with exo-miR-613 and corresponding exo-negative control (NC), we found overexpression of miR-613 remarkably increased the inhibition of cell proliferation induced by cisplatin. Exo-miR-613 fused into cells to significantly enhance the inhibited effect of DDP on the proliferation, migration and showed a promotion on cell apoptosis and DNA damage. The in vivo study showed that exo-miR-613 significantly inhibited the tumor growth, and promote the sensitivity to DDP, probably by down-regulating the expressions of GJA1, TBP and EIF-4E in tumor cells and tissues.
Conclusion: Exo-miR-613 reversed chemoresistance to DDP in NSCLC cell to involve in the process of tumor progression, and might be a potential therapeutic strategy for NSCLC.
Keywords: exosome, miRNA, non-small cell lung cancer, cisplatin, chemoresistance, apoptosis