108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于薯蓣皂苷的 pH 敏感型前药纳米载体用于阿霉素递送,可以有效抑制肿瘤转移
Authors Wei Z, Wang H, Xin G, Zeng Z, Li S, Ming Y, Zhang X, Xing Z, Li L, Li Y, Zhang B, Zhang J, Niu H, Huang W
Received 20 February 2020
Accepted for publication 17 July 2020
Published 4 September 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 6545—6560
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S250549
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
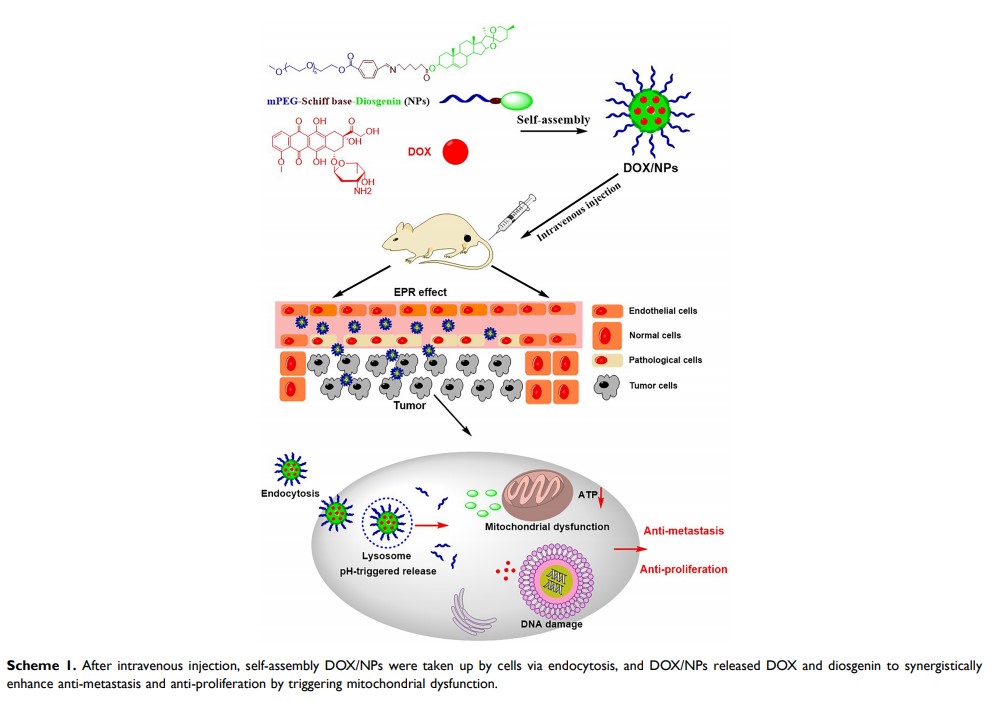
Background: The metastasis, one of the biggest barriers in cancer therapy, is the leading cause of tumor deterioration and recurrence. The anti.-metastasis has been considered as a feasible strategy for clinical cancer management. It is well known that diosgenin could inhibit tumor metastasis and doxorubicin (DOX) could induce tumor apoptosis. However, their efficient delivery remains challenging.
Purpose: To address these issues, a novel pH-sensitive polymer-prodrug based on diosgenin nanoparticles (NPs) platform was developed to enhance the efficiency of DOX delivery (DOX/NPs) for synergistic therapy of cutaneous melanoma, the most lethal form of skin cancer with high malignancy, early metastasis and high mortality.
Methods and Results: The inhibitory effect of DOX/NPs on tumor proliferation and migration was superior to that of NPs or free DOX. What is more, DOX/NPs could combine mitochondria-associated metastasis and apoptosis with unique internalization pathway of carrier to fight tumors. In addition, biodistribution experiments proved that DOX/NPs could efficiently accumulate in tumor sites through enhancing permeation and retention (EPR) effect compared with free DOX. Importantly, the data from in vivo experiment revealed that DOX/NPs without heart toxicity significantly inhibited tumor metastasis by exerting synergistic therapeutic effect, and reduced tumor volume and weight by inducing apoptosis.
Conclusion: The nanocarrier DOX/NPs with satisfying pharmaceutical characteristics based on the establishment of two different functional agents is a promising strategy for synergistically enhancing effects of cancer therapy.
Keywords: anti-metastasis, antitumor, self-assembly, codelivery, doxorubicin