108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

冬凌草甲素通过靶向 Akt 信号通路使肝细胞癌对索拉非尼的抗癌作用敏感
Authors Li X, Chen W, Liu K, Zhang S, Yang R, Liu K, Li D, Huang Y
Received 15 April 2020
Accepted for publication 18 August 2020
Published 7 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 8081—8091
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S257482
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Background: Oridonin is the core bioactive component of Rabdosia rubescens , a traditional Chinese herbal medicine used in the treatment of hepatoma. Sorafenib, a targeted therapeutic agent for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), has recently been shown to exert limited clinical effects. However, few studies have focused on the synergistic effect of these two drugs on hepatocellular carcinoma.
Methods: We treated different HCC cell lines with different concentrations of oridonin and sorafenib and assessed the viability by using MTT assays and examined proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis after cotreatment of HepG2 cells with 20 μM oridonin and 5 μM sorafenib via colony formation assays, Transwell assays and flow cytometry. Regulatory effects were measured by Western blotting. The in vivo synergistic effect was confirmed through xenograft tumor models, and tumor tissues were analyzed by immunohistochemistry.
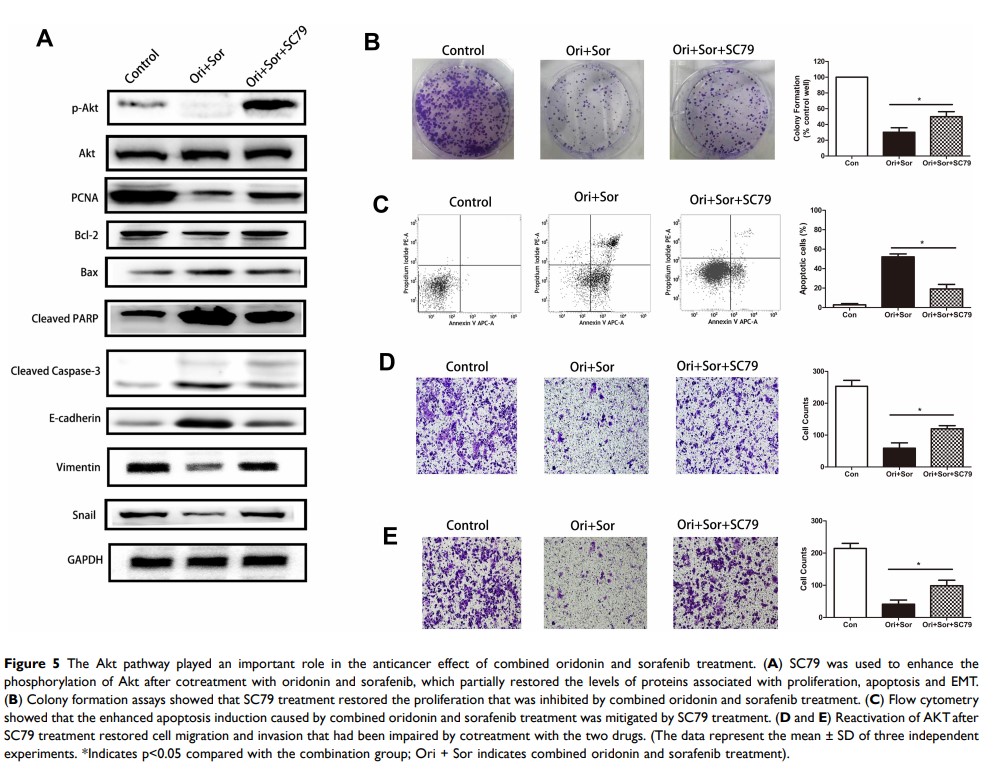
Results: The inhibitory effects of oridonin and sorafenib cotreatment on HCC cells were stronger than those of either drug alone. In addition, combined treatment with the two drugs synergistically inhibited epithelial–mesenchymal transition and the Akt pathway but not NF-κB or MAPK signaling. Akt phosphorylation by SC79 reversed the inhibitory effects of the combined treatment. Synergistic inhibition was equally observed in vivo.
Conclusion: Oridonin combined with sorafenib synergistically inhibited proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition and induced apoptosis by targeting the Akt pathway but not NF-κB or MAPK signaling.
Keywords: oridonin, sorafenib, HCC, Akt pathway