108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

纤维蛋白原和淋巴细胞计数在中度和高风险胃肠道间质瘤中的预后价值
Authors Guo Y, Liu J, Zhang W, Xiao S, Zheng G, Liu S, Guo M, Zhang H, Feng F
Received 13 May 2020
Accepted for publication 20 August 2020
Published 8 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 8149—8157
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S262570
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Purpose: Data about the prognostic value of fibrinogen concentration and absolute lymphocyte count for the prognosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) were limited. Thus, the aim of the present study was to investigate the predictive value of preoperative fibrinogen concentration and absolute lymphocyte count in GISTs.
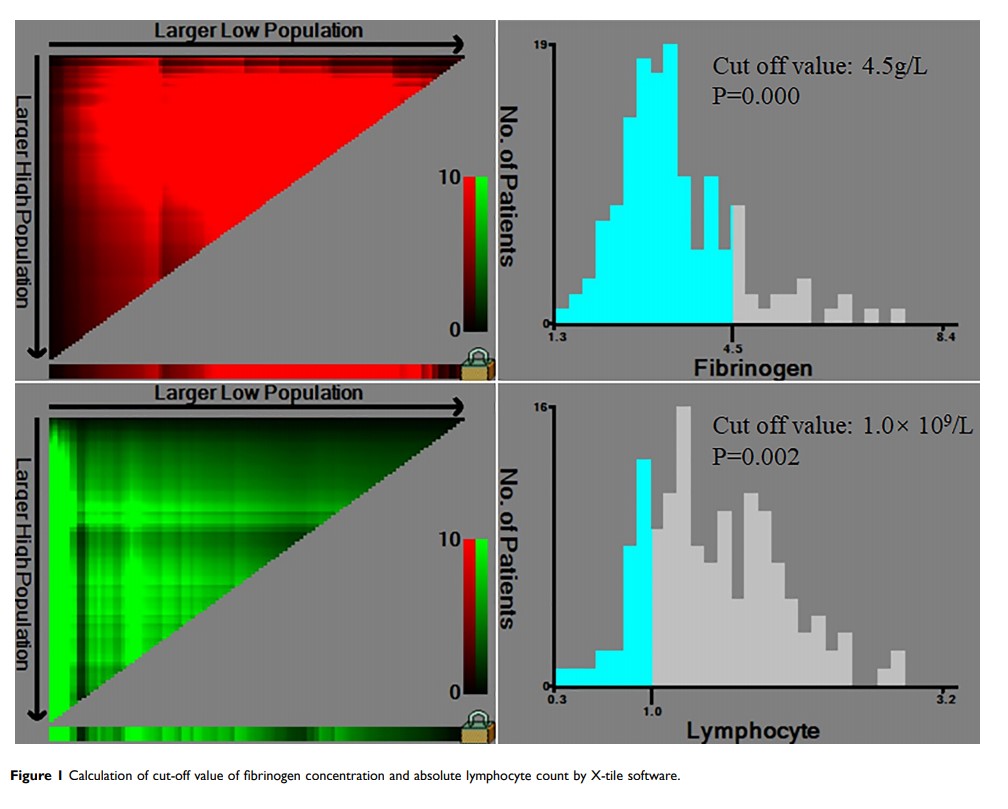
Patients and Methods: From March 2002 to December 2017, 143 intermediate and high risk GIST patients treated with R0 resection were enrolled in the present study. Clinicopathological characteristics were recorded. The optimal cut-off values of patients were calculated by X-tile software. Categorical variables were analyzed using Chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test. Disease-free survival was analyzed by the Kaplan–Meier method and compared by a Log rank test.
Results: There were 71 males (49.65%) and 72 females. The median age was 56 years (range 19– 86). The optimal cut-off value was 4.5 g/L for fibrinogen concentration (P=0.000) and 1.0× 109/L for lymphocyte count (P=0.002). No significant association was found between lymphocyte level and clinicopathological features. However, elevated fibrinogen level was correlated with tumor location, tumor size and NIH risk category. Tumor size, fibrinogen concentration and lymphocyte count were independent risk factors for the prognosis of patients according to the multivariate analysis. The prognosis of patients with high fibrinogen concentration or low lymphocyte count was significantly worse than that with low fibrinogen concentration or high lymphocyte count. Further, combination of fibrinogen concentration and lymphocyte count could increase the prognostic value for GIST patients.
Conclusion: Fibrinogen concentration and absolute lymphocyte count were independent prognostic factors for intermediate and high risk GIST patients. The combination of fibrinogen concentration and absolute lymphocyte count could further increase the predictive value for the prognosis of GIST patients.
Keywords: gastrointestinal stromal tumors, GIST, mesenchymal tumor, fibrinogen, lymphocyte, prognosis