108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

胃癌中放射敏感性基因和 CD19 状态的预后价值:使用 TCGA 数据库进行的回顾性研究
Authors Liang LB, Huang XY, He H, Liu JY
Received 10 June 2020
Accepted for publication 11 August 2020
Published 8 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 365—373
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PGPM.S265121
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Martin Bluth
Background: The correlation between the radiosensitivity genes combined with CD19 status and clinical outcome was investigated to identify gastric cancer (GC) patients who would benefit from radiotherapy combined with CAR-T cell therapy.
Methods: The gene expression and clinical features were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Stomach Cancer (STAD). To identify the hub radiosensitivity genes and CD19 status, 407 patients were categorized into two groups: radiosensitivity (RS) and radioresistance (RR) based on the prognosis. The chi-square test, Mann–Whitney test, and Kaplan–Meier survival analysis were applied to compare the differential expression in these groups and analyze the correlation between the gene expression and clinical outcome and features. Finally, the influencing factors for the prognosis of GC were investigated by multiple Cox regression, especially in RS patients.
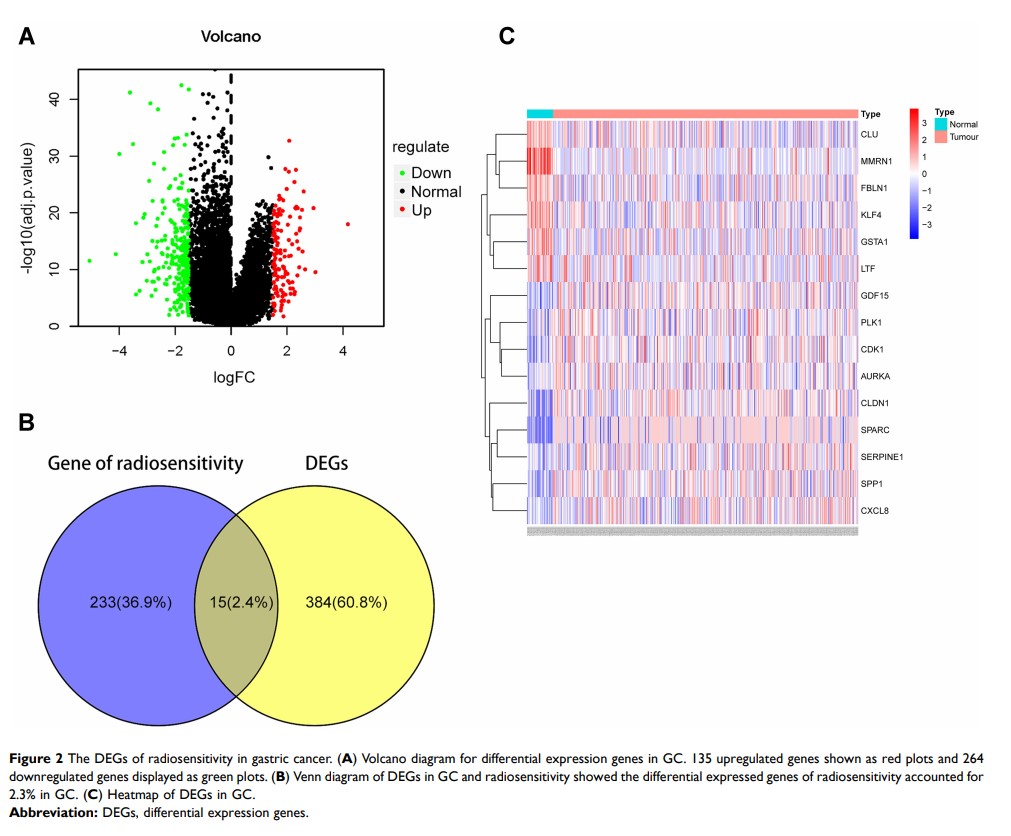
Results: A total of 15 differential expression genes, containing two communities with 8 hub radiosensitivity genes, were identified. We also identified a 2-gene signature model with a negative coefficient and calculated the risk score for the prognosis of GC. Also, Helicobacter pylori infection was validated, and the high-risk score of radiosensitivity genes was the risk factor, and high CD19 expression was the protective factor for the prognosis.
Conclusion: The radiosensitivity gene signature and CD19 expression predicted the clinical outcome of GC patients.
Keywords: gastric cancer, radiosensitivity genes, CAR-T cell therapy, TCGA database