108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA RMRP 通过 miR-613/NFAT5 轴促进非小细胞肺癌的细胞增殖和侵袭
Authors Yang M, Ke H, Zhou W
Received 23 March 2020
Accepted for publication 11 August 2020
Published 8 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 8941—8950
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S255126
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
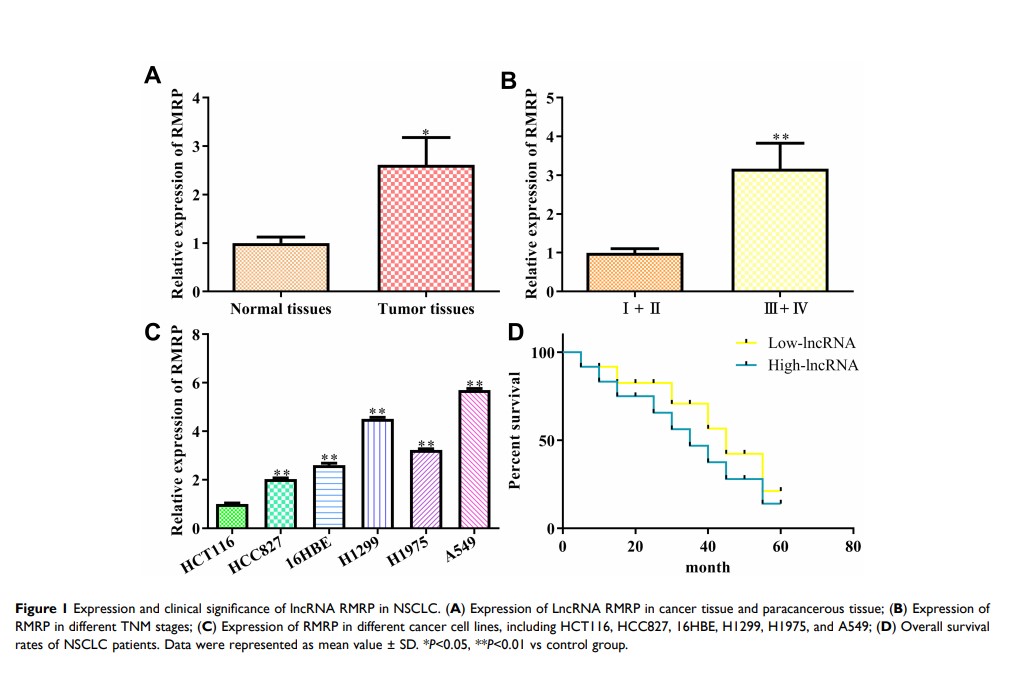
Background: The abnormal expression of RMRP and miR-613 was respectively associated with the pathogenesis of lung cancer, but the role of the RMRP/miR-613 axis in NSCLC has not been studied.
Methods: In this report, we measured the levels of RMRP in clinical NSCLC samples and cell lines. The target gene of RNA was predicted by online tools and verified by Luciferase reporter assay. Moreover, the function and regulatory mechanism of RMRP in the progression of cancer were further investigated.
Results: Our data showed that the expression of RMRP in NSCLC tissues and cell lines was both up-regulated. Functionally, RMRP promoted the proliferation and metastasis of A549 and H1299 cells. Luciferase reporter assay confirmed that RMRP was the sponger of miR-613, and NFAT5 is the direct target of miR-613. Functional acquisition and loss-of-function strategies further confirmed that RMRP induces the up-regulation of NFAT5 expression through competitive binding with miR-613, leading to promote the progression and metastasis potential of lung cancer cells.
Conclusion: Collectively, our findings emphasized the importance of RMRP in the development of NSCLC, which may provide a new therapeutic target and potential diagnostic biomarker for NSCLC therapy.
Keywords: NSCLC, RMRP, miR-613, NFAT5, sponge