108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在调强放疗的时代,嗅神经母细胞瘤的疗效和最佳治疗方案:单中心经验
Authors Liu T, Sun Q, Qin W, Chen X, Hu Q
Received 25 April 2020
Accepted for publication 4 August 2020
Published 10 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 8355—8362
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S259921
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Purpose: Esthesioneuroblastoma (ENB) is a type of rare malignant neoplasm of the sinonasal cavity. Optimal treatment for ENB is still controversial. A retrospective study was conducted to identify the clinical outcome and optimal treatment for ENB in the era of intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT).
Patients and Methods: Between December 2006 and August 2018, 37 patients with ENB without distant metastasis who underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by chemoradiotherapy (C+RC) or surgery followed by radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy (S+R/RC) were retrospectively reviewed at our center.
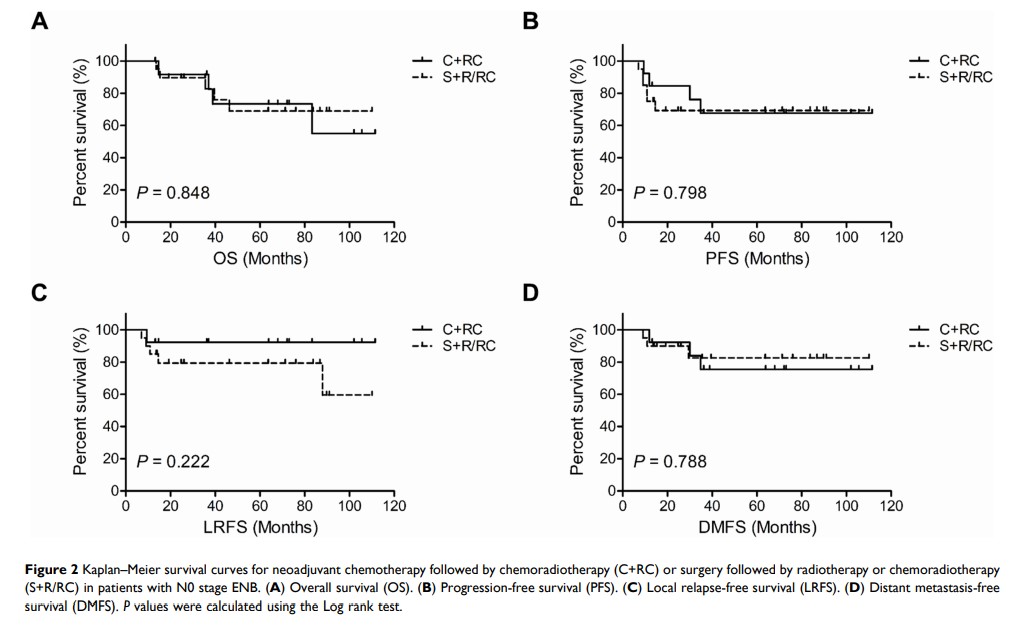
Results: The median follow-up period was 63.7 months (range, 13.2– 111.5 months). Five-year overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), locoregional relapse-free survival (LRFS), and distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) were similar between treatment arms (P values > 0.05). With a multivariate analysis, a Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) of ≤ 80 was a prognostic factor for poor five-year OS. A KPS of ≤ 80 and Kadish class C–D tumors were prognostic factors for poor PFS. A KPS of ≤ 80 was a prognostic factor for poor LRFS. When KPS was ≤ 80 and tumors were Kadish class C–D, T3– 4 and N1 were prognostic factors for poor DMFS. Subgroup analyses also demonstrated that the two treatment arms exhibited similar trends for OS, PFS, LRFS, and DMFS, excluding patients with N1 or Kadish class A–B tumors (P values > 0.05).
Conclusion: In the era of IMRT, S+R/RC failed to improve the outcomes of patients with ENB. C+RC may be a feasible treatment option for patients with ENB.
Keywords: olfactory neuroblastoma, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, precise radiotherapy