108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过共同的基因表达谱鉴定 FADS1,以预测膀胱癌患者的存活率
Authors Jiao F, Sun H, Yang Q, Sun H, Wang Z, Liu M, Chen J
Received 17 March 2020
Accepted for publication 5 August 2020
Published 10 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 8325—8339
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S254316
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
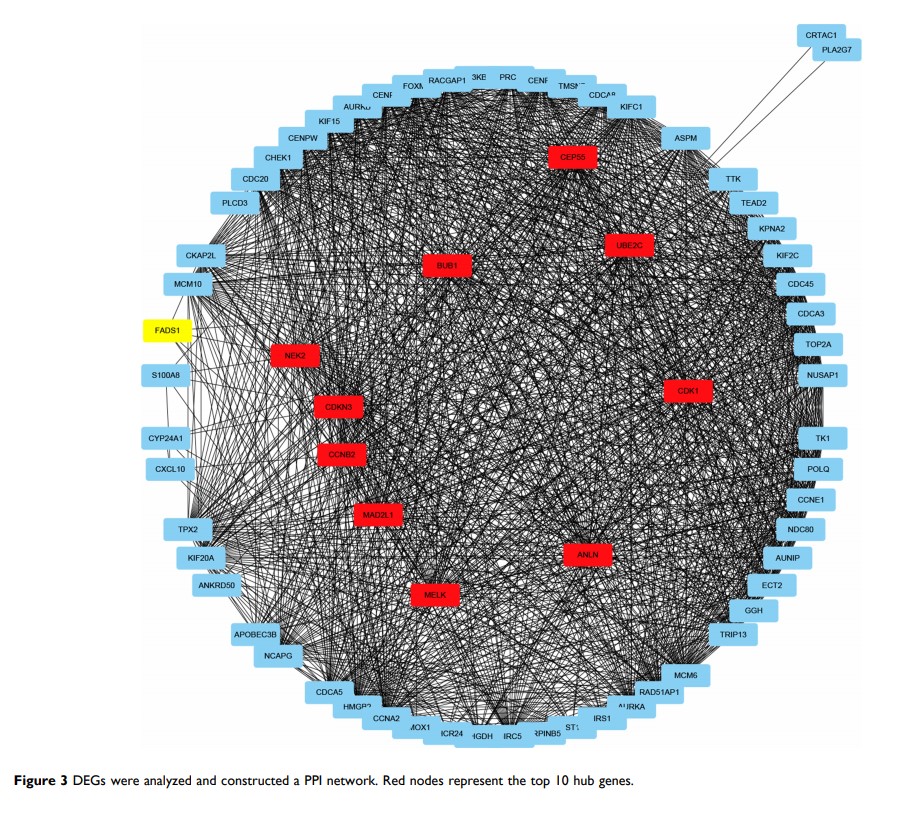
Purpose: Aim of this study was to identify biomarkers between different grades of bladder cancer (BLCA) and its prognostic value.
Methods: mRNA expression data from GSE32549 and GSE71576 were extracted for further analysis. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified using GEO2R web tool. Gene ontology (GO) analysis, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis and protein–protein interaction (PPI) network were conducted to explore the function and relationship of DEGs. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database was used for external validation and Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) analysis was used to further identify FADS1 pathways. Bladder cancer cells and patient specimens were used to further demonstrate the function of FADS1.
Results: Datasets from GEO identified a panel of DEGs. Functional enrichment analysis highlighted that DEGs were associated with nuclear division, spindle, cell cycle and p53 signaling pathway. External validation from TCGA demonstrated that FADS1 was an independent prognostic marker in BLCA patients. In cell lines and tumor specimen analysis, FADS1 was overexpressed in the tumor specimen, compared with adjacent tissues, and positively correlated with tumor grade of BLCA. Moreover, FADS1 could enhance the proliferation ability and influence cell cycle of bladder cancer cells.
Conclusion: FADS1 was an independent prognostic biomarker for BLCA and could confer the bladder cancer cells increased proliferation ability.
Keywords: FADS1, bioinformatics, bladder cancer, TCGA, proliferation