108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

负载多西他赛的适体引导的白蛋白纳米颗粒用于靶向治疗结肠癌
Authors Yu Z, Li X, Duan J, Yang X
Received 10 June 2020
Accepted for publication 10 August 2020
Published 11 September 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 6737—6748
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S267177
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yan Shen
Purpose: Chemotherapy of colon cancer needs improvement to mitigate the severe adverse effects (AEs) associated with the cytotoxic drugs. The aim of this study is to develop a novel targeted drug delivery system (TDDS) with practical application potential for colon cancer treatment.
Methods: The TDDS was built by loading docetaxel (DTX) in albumin nanoparticles (NPs) that were functionalized with nucleolin-targeted aptamers (AS1411).
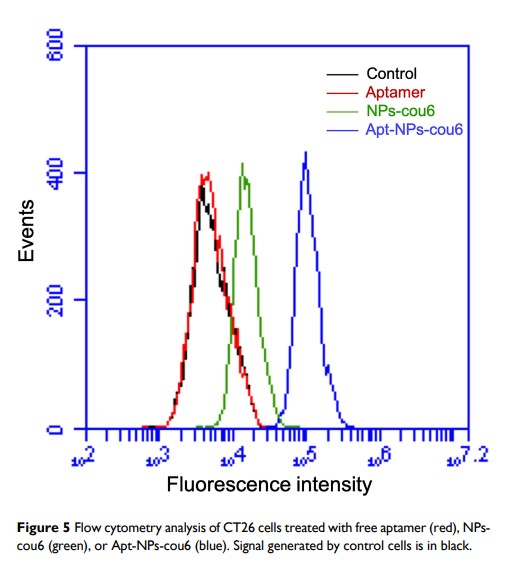
Results: The TDDS (Apt-NPs-DTX) had an average size of 62 nm and was negatively charged with a zeta potential of − 31.2 mV. DTX was released from the albumin NP with a typical sustained release profile. Aptamer-guided NPs were preferentially ingested by nucleolin-expressing CT26 colon cancer cells vs the control cells. In vitro cytotoxicity study showed that Apt-NPs-DTX significantly enhanced the killing of CT26 colon cancer cells. Importantly, compared with non-targeted drug delivery, Apt-NPs-DTX treatment significantly improved antitumor efficacy and prolonged the survival of CT26-bearing mice, without raising systemic toxicity.
Conclusion: The results suggest that Apt-NPs-DTX has potential in the targeted treatment of colon cancer.
Keywords: aptamer, nanoparticles, colon cancer, targeted drug delivery system