108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

癌细胞-红细胞杂化膜包覆的金纳米笼用于乳腺癌的近红外光激活的光热/放射/化疗
Authors Sun M, Duan Y, Ma Y, Zhang Q
Received 5 June 2020
Accepted for publication 24 August 2020
Published 11 September 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 6749—6760
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S266405
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
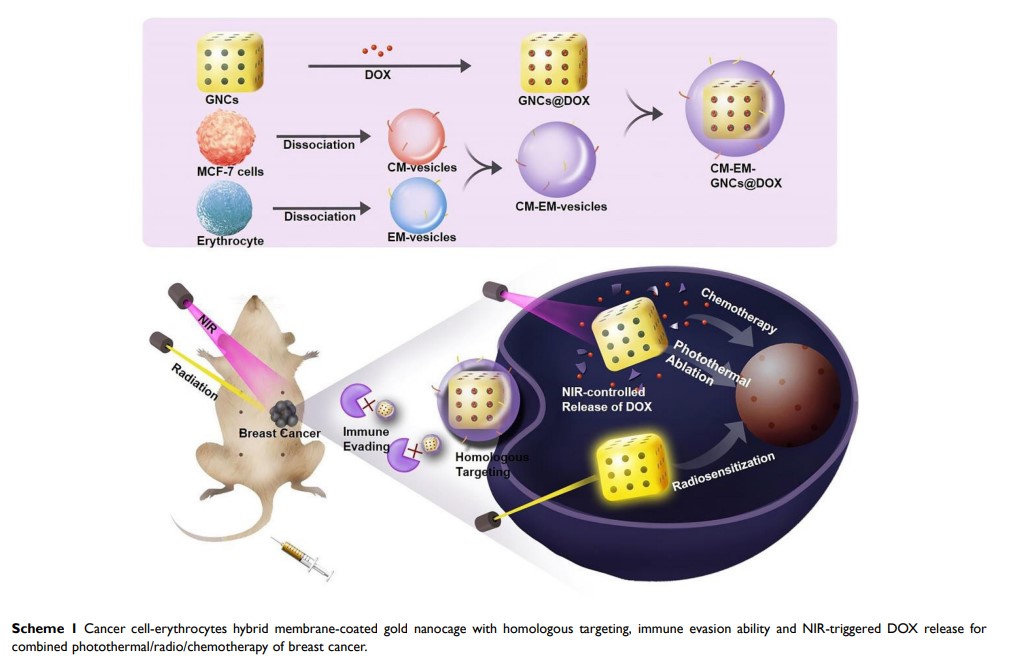
Background: The combination of radiotherapy (RT) and chemotherapy, as a standard treatment for breast cancer in the clinic, is unsatisfactory due to chemoradioresistance and severe side effects.
Methods and Results: To address these issues, a cancer cell-erythrocyte hybrid membrane-coated doxorubicin (DOX)-loaded gold nanocage (CM-EM-GNCs@DOX) was constructed for near-infrared light (NIR)-activated photothermal/radio/chemotherapy of breast cancer. CM-EM-GNCs@DOX inherited an excellent homologous target ability from the cancer cell membrane and an immune evasion capability from the erythrocyte membrane, together resulting in highly efficient accumulation in the tumor site with decreased clearance. Following the highly efficient uptake of CM-EM-GNCs@DOX in cancer cells, the RT efficacy was remarkably amplified due to the radiosensitization effect of CM-EM-GNCs@DOX, which reduced the needed radiotherapeutic dose. Importantly, with NIR irradiation, CM-EM-GNCs@DOX exerted a high photothermal effect, which not only ruptured CM-EM-GNCs@DOX to release DOX for precise and controllable chemotherapy, but also potentiated chemo/radiotherapy by photothermal therapy.
Conclusion: Therefore, a highly efficient and safe combined photothermal/radio/chemotherapy approach was achieved in vitro and in vivo by CM-EM-GNCs@DOX, which provided a promising strategy for treating breast cancer.
Keywords: gold nanocages, biomimetic, cancer cell-erythrocyte, radiation sensitization, combined therapies, breast cancer