108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

白藜芦醇和替莫唑胺对胶质母细胞瘤细胞的协同作用:潜在的机制和治疗意义
Authors Liu Y, Song X, Wu M, Wu J, Liu J
Received 17 April 2020
Accepted for publication 16 July 2020
Published 11 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 8341—8354
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S258584
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
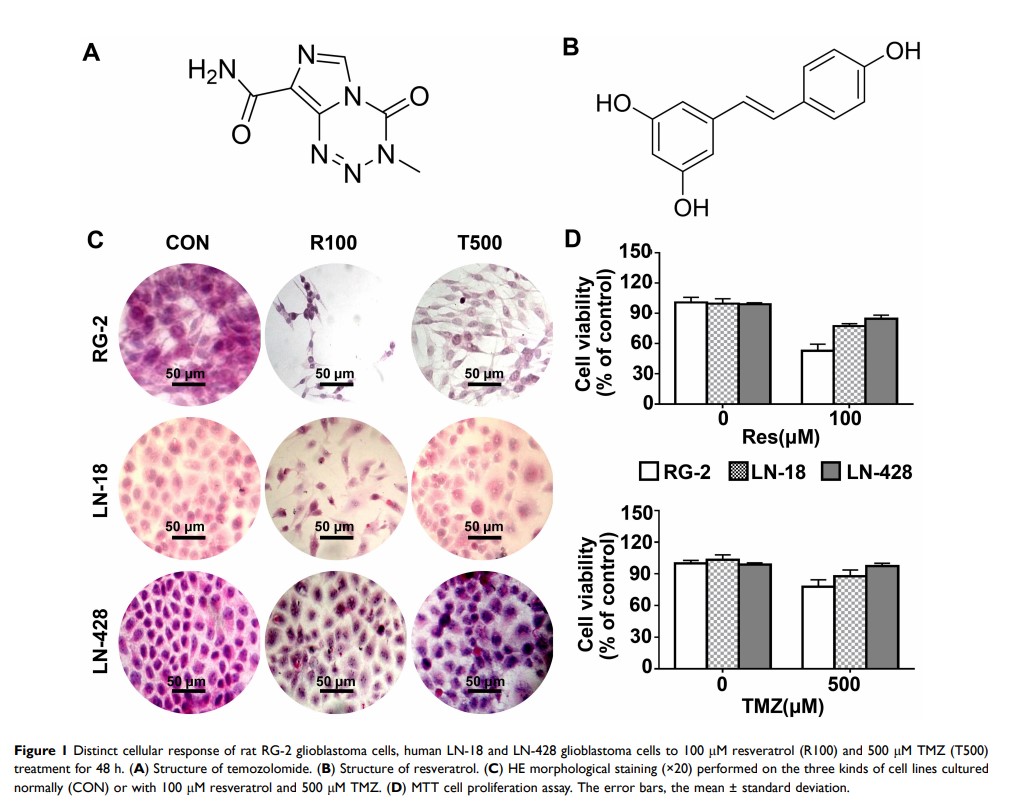
Purpose: Temozolomide (TMZ) is a commonly used anti-glioblastoma (GBM) drug. However, glioblastoma cells frequently show primary and acquired resistance to TMZ. As a promising anti-GBM candidate, resveratrol (Res) faces the similar problem as TMZ. Although resveratrol combined with TMZ (Res/TMZ) has been reported to be used to treat GBMs, it remains unclear whether this combination is broad-spectrum for all glioma cells until now, especially for GBM cells/cases with dual drug resistance. The study aimed to evaluate the synergistic effects of resveratrol and TMZ against GBMs and identify the underlying mechanisms.
Materials and Methods: Drug sensitivities of rat RG-2, human LN-18 and LN-428 cell lines and effectiveness of Res/TMZ combinations were investigated via multiple experimental methods. O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) was observed by Western blotting and immunocytochemistry (ICC). Transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway and expression changes of STAT3 -related gene were detected to explore the possible synergistic mechanism.
Results: One hundred micromolar resveratrol and 500 μM TMZ inhibited the growth of RG-2 cells and the low-dose combination (25 μM/250 μM) showed similar suppressive effects. LN-18 and, especially, LN-428 cells were neither sensitive to 100 μM resveratrol nor to 500 μM TMZ, while their growth was suppressed by combination of 75 μM Res/750 μM TMZ with the suppressive rates of 62.5% and 28.6% and apoptosis rates of 11.9% and 7.4%, respectively. Resveratrol had regulatory effect on the expression of MGMT and it could significantly down-regulate MGMT overexpression caused by TMZ. In addition, STAT3/Bcl-2/survivin signaling pathway was also remarkably inhibited in Res/TMZ-treated GBM cells.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrated synergistic effects of Res/TMZ on RG-2 cells and their bilaterally sensitizing effects to LN-18 and LN-428 cells. Frequent upregulation of MGMT and activation of STAT3 are the unfavorable factors for the treatment of GBMs and they may be the potential targets of Res/TMZ therapy.
Keywords: resveratrol, temozolomide, synergistic effects, glioblastoma, MGMT, STAT3, Bcl-2, survivin