108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

化疗对中国乳腺癌术后患者血脂的影响
Authors Lu Q, Wu X, Zhu Y, Yang J, Wang X, Ye C, Cai R, Zhang K, Xu T, Wang B, Veeramootoo JS, Xia T, Liu X
Received 25 May 2020
Accepted for publication 11 August 2020
Published 11 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 8397—8408
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S253397
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Seema Singh
Purpose: Chemotherapy is a comprehensive therapy for breast cancer; nevertheless, its associated adverse effects are drawing increasing attention with the continuous improvement of the efficacy. The changes in serum lipids of breast cancer patients caused by chemotherapy have been reported by previous studies, whereby the former increase the incidence rate of cardiovascular disorders. However, the variations in the changes of serum lipids with different chemotherapy regimens have seldom been reported.
Methods: From January 2011 to December 2017, 1740 breast cancer patients treated with chemotherapy were recruited at the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. The chemotherapy regimens included anthracycline-based, taxane-based, and anthracycline-plus-taxane-based regimens, dose-dense and standard-interval regimens. Lipid profiles that contained TG (triglyceride), TC (total cholesterol), HDL-C (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol), LDL-C (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol) and Lpa (lipoprotein a) levels were collected prior to the first, second and last cycles of chemotherapy. The changes of serum lipids with the same or different chemotherapy regimens were analyzed and compared.
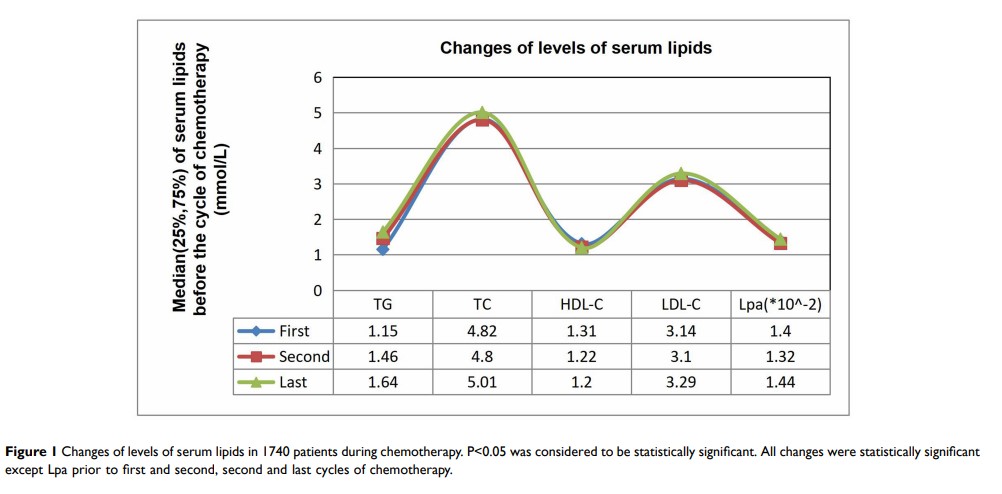
Results: It was observed that the levels of TG, TC, LDL-C and Lpa increased significantly while that of HDL-C decreased after adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients (P< 0.05). Besides, dose-dense regimens had more influence in TG and HDL-C and less influence in TC and LDL-C than standard-interval regimens. HDL-C was more sensitive to anthracycline-based regimens than taxane-based regimens. The level of TG with anthracycline-plus-taxane-based regimens was higher than that with only anthracycline-based or taxane-based regimens, and the level of HDL-C with anthracycline-plus-taxane-based regimen showed lower than that with taxane-based regimen.
Conclusion: In summary, this study proposed that dyslipidemia was strongly associated with chemotherapy in Chinese breast cancer patients after operative treatment. Furthermore, the changes in levels of serum lipids varied among patients with different chemotherapy regimens and taxane had less effect on dyslipidemia than anthracycline.
Keywords: breast cancer, serum lipids, dyslipidemia, chemotherapy, treatment