108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肿瘤相关内皮细胞分泌的 HSPA12B 可通过激活 PI3K/Akt/mTOR 信号传导诱导巨噬细胞的 M2 极化
Authors Zhou J, Zhang A, Fan L
Received 22 March 2020
Accepted for publication 7 August 2020
Published 11 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 9103—9111
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S254985
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Purpose: The intratumoral microenvironment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSC) is highly immunosuppressive. In this study, we explored the potential functional role of HSPA12B secreted by tumor-associated endothelial cells (TECs) in M2 polarization of macrophages.
Materials and Methods: Bulk-seq data from TCGA-HNSC and single-cell RNA-seq data from GSE103322 (with over 5000 cells from 18 primary HNSC cases) were used for bioinformatic analysis. RAW264.7 cell line was used for in vitro studies.
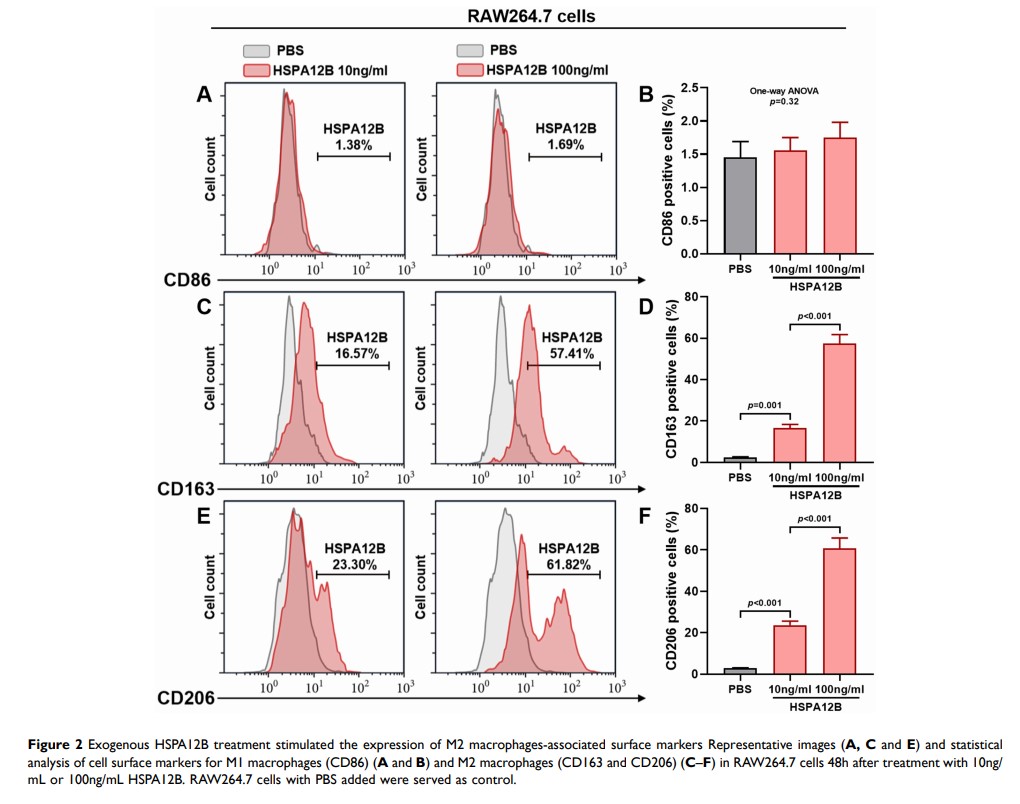
Results: TECs in HNSC had significantly higher expression and secretion of HSPA12B, compared to normal human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Exogenous HSPA12B treatment increased the expression of M2 macrophage marker CD163 and CD206 on RAW264.7 cells in a dose-dependent manner but had no significant influence on CD86, an M1 macrophage marker. OLR1, a known receptor of HSP70 proteins, was specifically expressed in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in HNSC. OLR1 knockdown significantly impaired HSPA12B uptake by RAW264.7 cells and weakened HSPA12B-induced CD163 and CD206 upregulation. HSPA12B treatment increased the expression of p-PI3K, p-Akt and p-mTOR in a dose-dependent manner in RAW264.7 cells. OLR1 inhibition and LY294002 treatment significantly weakened the effects HSPA12B on activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling and M2 marker expression.
Conclusion: Based on these findings, we speculated that aberrantly expressed and secreted HSPA12B by TECs could be taken by macrophages partly via OLR1, leading to subsequent activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and elevated expression of M2 markers. This mechanism shows a novel cross-talk between TECs and TAMs, which contributes to the intratumoral immunosuppressive microenvironment.
Keywords: HSPA12B, OLR1 , head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, macrophage polarization