108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

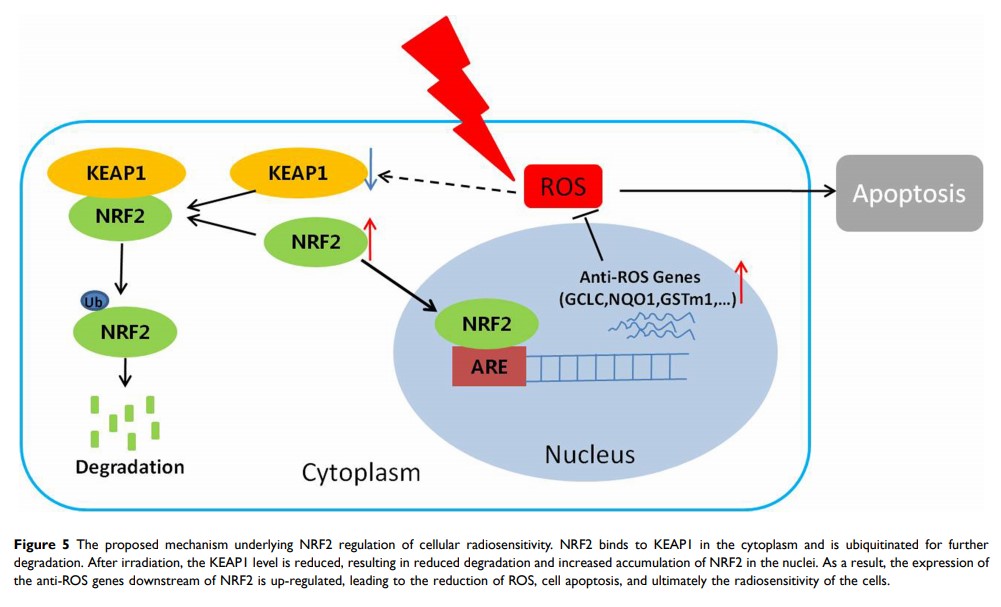
NRF2/KEAP1 信号通路通过清除 ROS 调节鼻咽癌细胞的放射敏感性
Authors Zhou J, Ding J, Ma X, Zhang M, Huo Z, Yao Y, Li D, Wang Z
Received 4 May 2020
Accepted for publication 8 August 2020
Published 11 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 9113—9122
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S260169
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Nicola Silvestris
Purpose: Radioresistance is a vital obstacle for the prognosis of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), but the underlying mechanism is still unknown. Here, we explored the role of the NRF2/KEAP1 pathway in radioresistance of NPC cell lines.
Materials and Methods: We selected NPC cell lines CNE-1 and CNE-2, treated them with ionization, and subsequently determined the levels of NRF2, KEAP1, antioxidant enzymes, and ROS. We then evaluated the effect of NRF2 or KEAP1 inhibition on cell proliferation, colony formation, and radiosensitivity in CNE2 cells.
Results: We discovered that the NRF2/KEAP1 signaling pathway can be activated by radiotherapy in NPC cells, while NRF2 knockdown enhances the sensitivity of CNE-2 cells to radiation treatment. In contrast, the silencing of KEAP1 inhibits the sensitivity of CNE-2 cells to radiation treatment.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that NRF2/KEAP1 signaling may serve as an essential regulator of the radioresistance of NPC and may be applied as a novel therapeutic approach for the sensitization of NPC to radiation.
Keywords: nasopharyngeal carcinoma, NRF2, KEAP1, radiosensitivity