108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

超声引导下单侧腹横肌平面阻滞联合腹直肌鞘阻滞与蛛网膜下腔麻醉用于腹膜透析导管手术患者的对比:一项随机前瞻性对照试验
Authors Li J, Guo W, Zhao W, Wang X, Hu W, Zhou J, Xu S, Lei H
Received 24 May 2020
Accepted for publication 1 August 2020
Published 14 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2279—2287
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S264255
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Robert B. Raffa
Background: Peritoneal dialysis catheter placement can be performed under general anesthesia, local anesthesia or subarachnoid anesthesia (SA). Recently, studies have reported the successful placement of peritoneal dialysis catheters using a transversus abdominis plane (TAP) block and rectus sheath (RS) block. This study compared the TAP + RS block with SA for patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis catheter placement.
Methods: Sixty patients were randomly divided into two groups, with 30 receiving unilateral ultrasound-guided TAP + RS block anesthesia and 30 receiving SA. The demographic characteristics, anesthesia efficacy, indicators related to anesthesia or operation, hemodynamic index, postoperative pain numeric rating score (NRS), postoperative recovery indicators, complications related to anesthesia or surgery, and dosage of sedative or analgesic medication were analyzed.
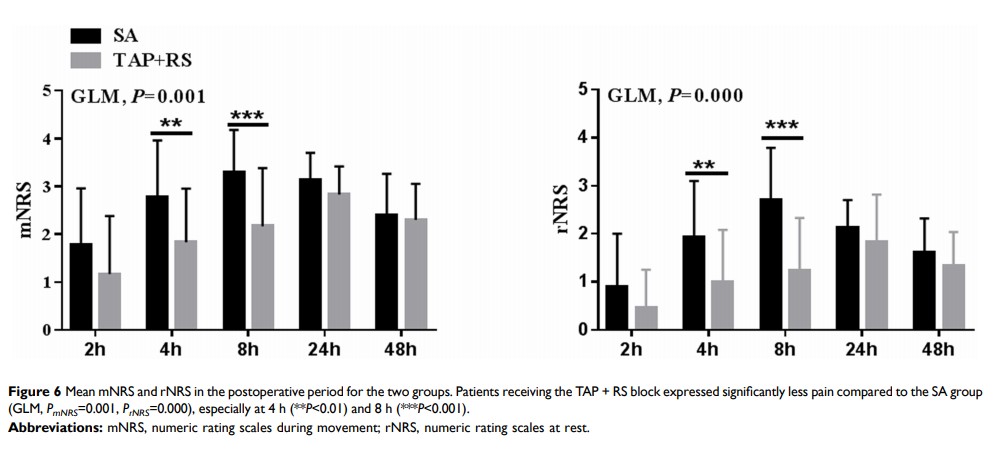
Results: Anesthesia operation time was significantly shorter in the TAP + RS block group than in the SA group (P < 0.001), while there was no significant difference in success rates (TAP + RS 93.33% [95% confidence interval, 95% CI, 83.9– 102.8%] vs SA 100.00% [95% CI, 100– 100%], P =0.472). Two patients in the TAP + RS group needed extra analgesia, although the dermatome pinprick sensation test gave negative results for all patients. Patients who received the TAP + RS block expressed significantly less pain on movement or at rest at 4 h and 8 h postoperative. Fewer patients needed rescue analgesia with tramadol in the postoperative period in the TAP + RS block group than in the SA group (P < 0.05). The intraoperative MAP was more stable (P < 0.05) in the TAP + RS group compared to the SA group.
Conclusion: The TAP + RS block is a safe, effective method for use as the principal anesthesia technique in PD catheter placement. Compared to SA, it has the advantages of less influence on hemodynamics and a better postoperative analgesic effect.
Keywords: TAP block, rectus sheath block, peritoneal dialysis catheter placement, local anesthesia, subarachnoid anesthesia