108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

采用 UPLC-MS/MS 方法测定艾沙康唑、伊曲康唑和氟康唑对 Selinexor 在大鼠体内药代动力学的影响
Authors Li S, Zhang Y, Cheng Q, Xin J, Dong Z, Qiu X
Received 29 June 2020
Accepted for publication 7 August 2020
Published 14 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3153—3161
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S269831
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Objective: An ultra performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) method for the determination of selinexor was established to investigate the effects of isavuconazole, itraconazole and fluconazole on the pharmacokinetics of selinexor in rats, respectively.
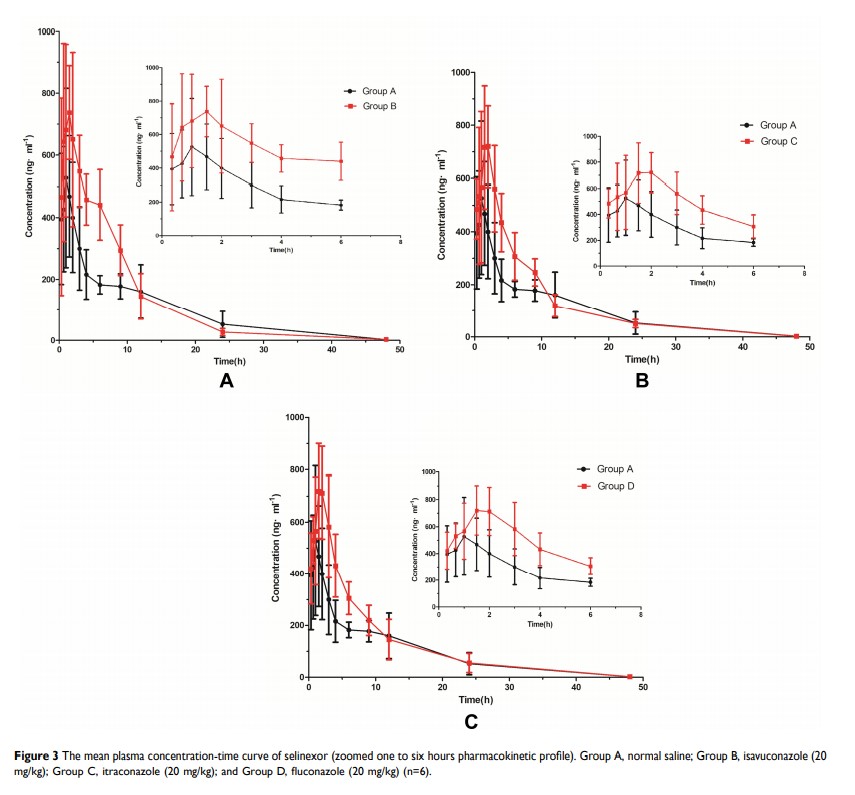
Methods: Twenty-four healthy male rats were randomly divided into four groups: group A, normal saline; group B, isavuconazole (20 mg/kg); group C, itraconazole (20 mg/kg); and group D, fluconazole (20 mg/kg). After 30 min of oral administration of normal saline, isavuconazole, itraconazole, and fluconazole, all the rats were given selinexor (8 mg/kg). The plasma concentration of selinexor was estimated by UPLC-MS/MS, and the pharmacokinetic parameters of selinexor were calculated by Drug and Statistics (DAS) 2.0 software.
Results: Under these experimental conditions, the method showed good linearity and stability. Intraday and interday accuracy and sample recovery were acceptable. Compared with group A, the Cmax, AUC(0−t) and AUC(0−∞) of selinexor in group B increased by 59.05%, 31.69%, and 31.45%; the Cmax, AUC(0−t) and AUC(0−∞) of selinexor in group C increased by 56.14%, 25.34%, and 25.08%; the Cmax, AUC(0−t) and AUC(0−∞) of selinexor in group D increased by 43.44%, 29.16%, and 31.96%, respectively. The Tmax of the experimental groups were extended, and CLz/F was also significantly reduced.
Conclusion: These results indicated that isavuconazole, itraconazole, and fluconazole have significant inhibitory effects on selinexor pharmacokinetics and increased selinexor plasma exposure in rats. Therefore, when these drugs were used in combination, clinicians should pay attention to the changes in treatment effects and the occurrence of adverse reactions caused by the drug-drug interactions.
Keywords: isavuconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, selinexor, UPLC-MS/MS, pharmacokinetics, drug-drug interactions