108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

经直肠超声引导前列腺系统穿刺活检后全身炎症反应综合征的病因和危险因素的回顾性研究
Authors Lei H, Dong X, Li L, Huan F, Zhong X, Wu Q, Fang H, Zhang T, Yang X, Zhu J, Li J, Jiang Z
Received 2 April 2020
Accepted for publication 18 July 2020
Published 15 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3187—3193
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S256548
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sahil Khanna
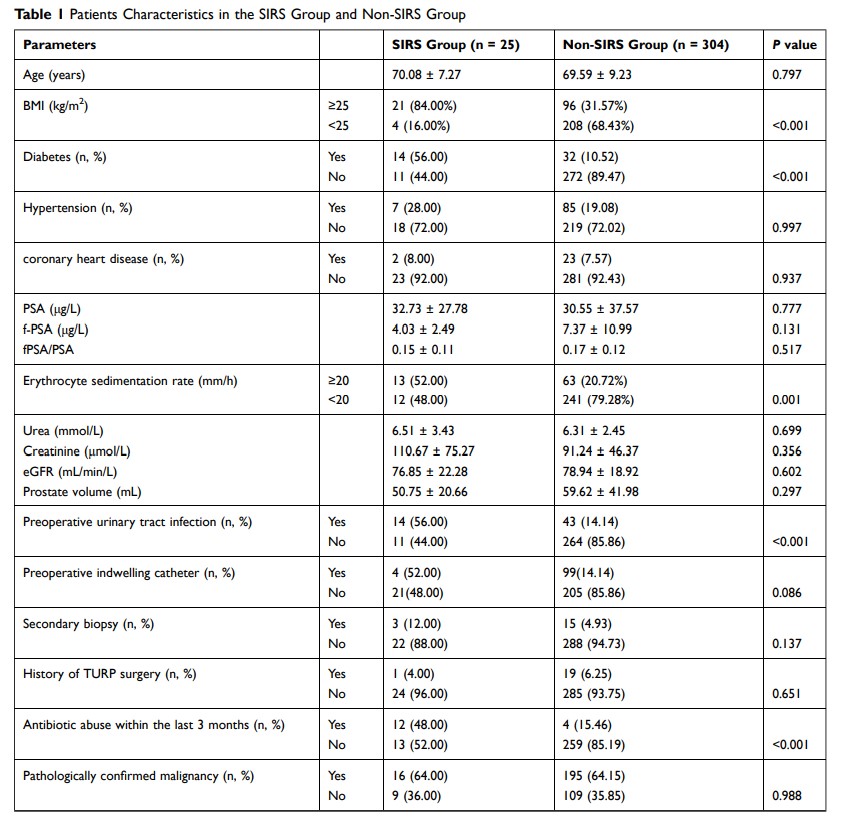
Objective: To explore the risk factors, pathogenic bacteria distribution and drug resistance of systematic transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy (TRUS-Bx), 329 cases of TRUS-Bx were collected, retrospectively, in the Second Affiliated Hospital, Army Military Medical University, from April 2017 to October 2019.
Methods: A total of 329 cases were all qualified and grouped into the SIRS group (25 cases) and the non-SIRS group (304 cases). Of all the cases, incidence and risk factors of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) were analyzed. Urine and blood samples of patients with SIRS after TRUS-Bx were also collected for bacterial culture and drug sensitivity test.
Results: Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 (OR = 1.66, 95% CI = 1.34– 2.12, P < 0.001), history of diabetes (OR = 5.48, 95% CI = 1.53– 19.68, P = 0.008), urinary infection before operation (OR = 9.19, 95% CI = 2.92– 20.93, P < 0.001) and erythrocyte sedimentation (ESR) ≥ 20 mm/h (OR = 1.04, 95% CI = 1.01– 1.08, P = 0.039) were independent risk factors of SIRS after TURS-PB.
Conclusion: The incidence of SIRS and urinary sepsis was 7.59% and 2.13%, respectively, and major pathogens of SIRS after TRUS-Bx were Escherichia coli (58.33%), Klebsiella pneumoniae (12.5%) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (12.5%). Imipenem, meropenem, tigecycline, piperacillin/tazobactam, teicoplanin, vancomycin, amikacin and cefoperazone/sulbactam had a very strong inhibitory effect to those pathogenic bacteria (sensitivity 85.72%∼ 100%). Levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin, penicillin G, compound neonomine and second-generation cephalosporins showed less but also worked as a good inhibitor to pathogenic bacteria (42.86%∼ 80.95%).
Keywords: systematic transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy, systemic inflammatory response syndrome, prostate cancer, risk factors infection, pathogens