108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

潜在的抗乙肝病药物 N -(4-氯苯基)-4-甲氧基-3-(甲氨基)苯甲酰胺的合成与生物活性
Authors Cui AL, Sun WF, Zhong ZJ, Jin J, Xue ST, Wu S, Li YH, Li ZR
Received 20 May 2020
Accepted for publication 2 September 2020
Published 15 September 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 3723—3729
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S263701
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yan Zhu
Introduction: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a global health concern that can cause acute and chronic liver diseases. Thus, there is an urgent need to research novel anti-HBV agents. Our previous reports show that N-phenylbenzamide derivatives exert broad-spectrum antiviral effects against HIV-1, HCV, and EV71 by increasing intracellular levels of APOBEC3G (A3G). As A3G is capable of inhibiting the replication of HBV, we screened the N-phenylbenzamide derivatives against HBV.
Methods: In this study, a new derivative, N -(4-chlorophenyl)-4-methoxy-3-(methylamino) benzamide (IMB-0523), was synthesized and its anti-HBV activity was evaluated in vitro and in vivo. The acute toxicity and pharmacokinetic profiles of IMB-0523 were also investigated.
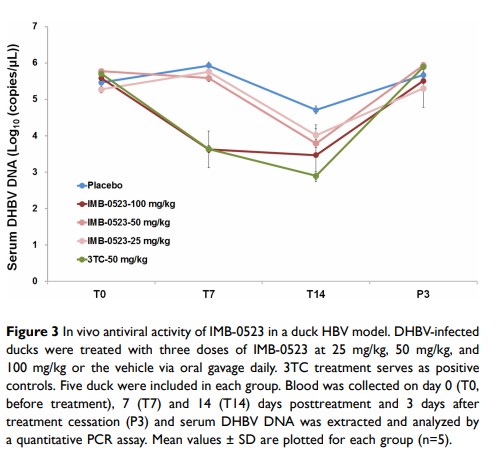
Results: Our results show that IMB-0523 has higher anti-HBV activity in both wild-type HBV (IC50: 1.99 μM) and drug-resistant HBV (IC50: 3.30 μM) than lamivudine (3TC, IC50: 7.37 μM in wild-type HBV, IC50: > 440 μM in drug-resistant HBV). The antiviral effect of IMB-0523 against HBV may be due to an increased level of intracellular A3G. IMB-0523 also showed low acute toxicity (LD50: 448 mg/kg) in mice and promising PK properties (AUC0-t: 7535.10± 2226.73 μg·h/L) in rats. Further, IMB-0523 showed potent anti-HBV activity in DHBV-infected ducks.
Conclusion: Thus, IMB-0523 may be a potential anti-HBV agent with different mechanisms than current anti-HBV treatment options.
Keywords: anti-HBV activity, APOBEC3G, hepatitis B virus, IMB-0523, PK, toxicity