108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

线粒体在慢性阻塞性肺疾病不同调节机制中的潜在作用
Authors Liu JY, Zhang MY, Qu YQ
Received 2 June 2020
Accepted for publication 12 August 2020
Published 15 September 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 2167—2177
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S265728
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr MeiLan K Han
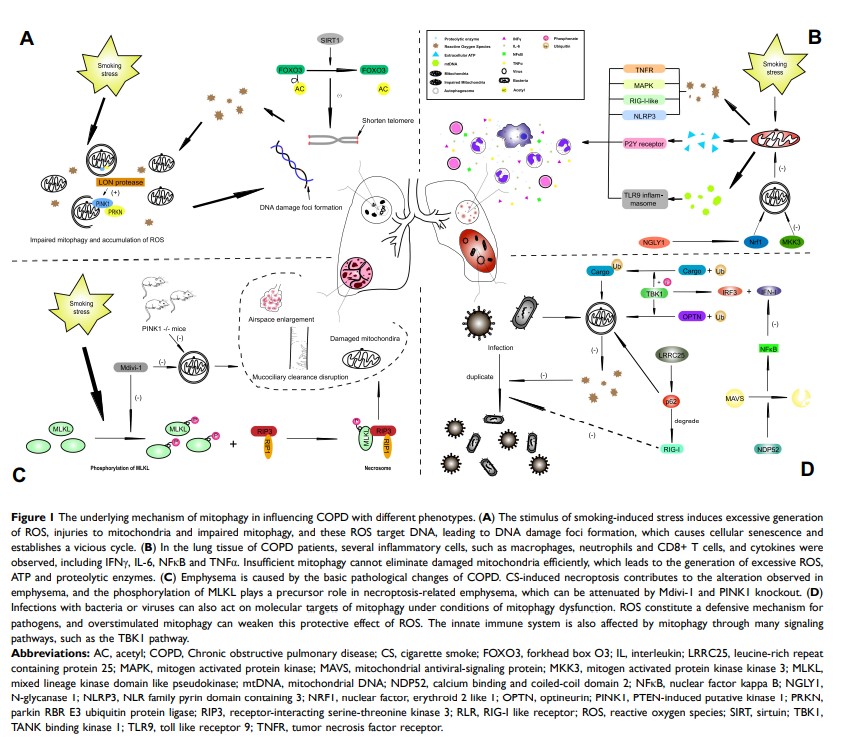
Abstract: COPD is a common disease of the respiratory system. Inflammation, cellular senescence and necroptosis are all pathological alterations of this disease, which may lead to emphysema and infection that aggravate disease progression. Mitochondria acting as respiration-related organelles is usually observed with abnormal changes in morphology and function in CS-stimulated models and COPD patients. Damaged mitochondria can activate mitophagy, a vital mechanism for mitochondrial quality control, whereas under the persistent stimulus of CS or other forms of oxidative stress, mitophagy is impaired, resulting in insufficient clearance of damaged mitochondria. However, the excessive activation of mitophagy also seems to disturb the pathology of COPD. In this review, we demonstrate the variations in mitochondria and mitophagy in CS-induced models and COPD patients and discuss the underlying regulatory mechanism of mitophagy and COPD, including the roles of inflammation, senescence, emphysema and infection.
Keywords: mitophagy, COPD, different regulatory mechanisms