108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国女性的骨矿物质密度与脂质分布之间的关联
Authors Zhang Q, Zhou J, Wang Q, Lu C, Xu Y, Cao H, Xie X, Wu X, Li J, Chen D
Received 8 June 2020
Accepted for publication 11 August 2020
Published 15 September 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 1649—1664
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S266722
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Zhi-Ying Wu
Purpose: Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease may share the risk factors for low bone mineral density (BMD), one of which is dyslipidemia. The association between serum cholesterol and BMD remains controversial. Thus, the correlation between serum lipids and BMD in women was explored in the current study.
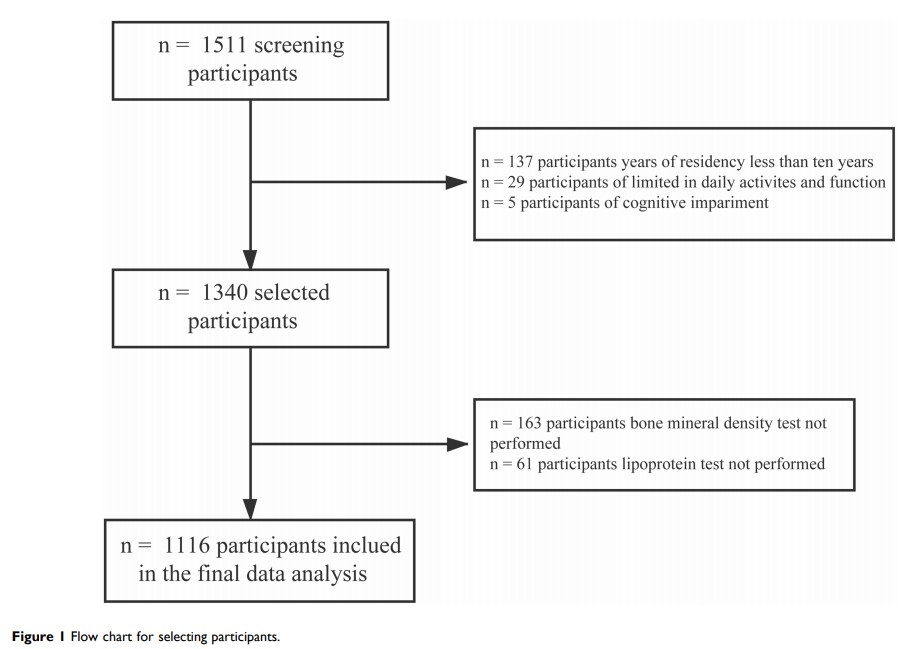
Materials and Methods: This cross-sectional study included 1116 Chinese female participants. Serum samples were collected to evaluate total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and other laboratory markers. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry was used to assess lumbar spine, femoral neck, and total hip BMD.
Results: In the postmenopausal women, a non-linear relationship was detected between TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, and lumbar spine BMD. Using segmented linear regression, the inflection points were 5.86 mmol/L, 3.52 mmol/L, and 2.37 mmol/L, respectively. To the left of the inflection point, the higher the serum lipid level, the lower the value for lumbar spine BMD. To the right of the inflection point, the higher the serum level of TC and LDL-C, the higher the value for lumbar spine BMD. In the premenopausal women, the association between HDL-C and femoral neck BMD was non-linear. In addition, LDL-C had a positive association with BMD of the femoral neck and HDL-C had an inverse association with BMD of the femoral neck in postmenopausal women.
Conclusion: In postmenopausal women, the relationship between TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, and lumbar spine BMD was non-linear. TC, LDL-C, and HDL-C were negatively associated with lumbar spine BMD when the values were less than 5.86 mmol/L, 3.52 mmol/L, and 2.37 mmol/L, respectively. The mechanisms of the association were unclear, and further research is warranted to clarify the relationship.
Keywords: serum lipids, bone mineral density, postmenopausal women, premenopausal women, cholesterol