108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中脑星形胶质细胞源性神经营养因子,是胆管癌的预后因子,通过使内质网应激恶化影响胆管癌细胞对索拉非尼敏感性
Authors He J, Li G, Liu X, Ma L, Zhang J, Zheng S, Wang J, Liu J
Received 10 January 2020
Accepted for publication 11 August 2020
Published 16 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 9169—9184
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S245575
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Jianmin Xu
Purpose: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) is an aggressive malignant tumor characterized by high malignancy and poor prognosis. Although the efficacy of sorafenib against cholangiocarcinoma cell lines has been demonstrated in vivo and in vitro, limited clinical data are available on the efficacy of sorafenib in patients with cholangiocarcinoma. Sorafenib can enhance endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-mediated apoptosis, and ER stress and unfolded protein response are also the mechanisms by which cancer cells resist drug therapy. Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF), initially identified as a neurotrophic factor, can be regulated by ER stress activation. There are no available studies on the diagnostic value and therapeutic significance of MANF in ICC. Hence, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the role of MANF in cholangiocarcinoma, investigating the possibility of whether sorafenib could become a reliable strategy for cholangiocarcinoma therapy.
Methods: In this study, the expression level of MANF in ICC patients was investigated by bioinformatic analysis and the results were verified by tissue microarray assay. Cholangiocarcinoma cell lines were also used to determine how MANF regulates the therapeutic effect of sorafenib and to identify the underlying mechanisms.
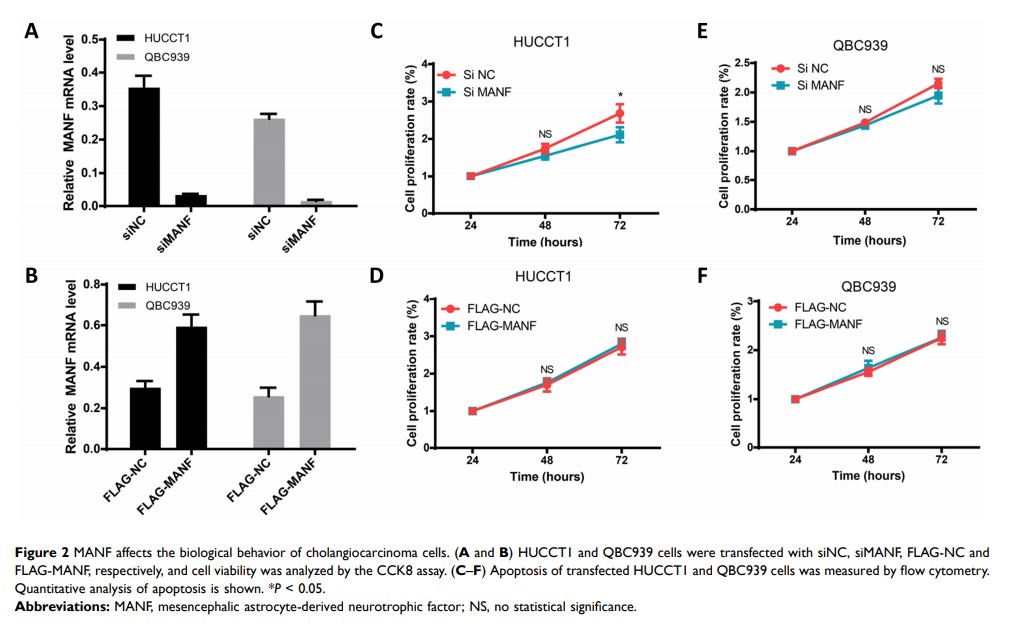
Results: The results showed that MANF was correlated with poor prognosis and MANF knockdown could facilitate sorafenib-mediated apoptosis and increase the sensitivity of sorafenib treatment by activating excessive ER stress.
Conclusion: MANF is a prognostic marker of cholangiocarcinoma. MANF knockdown increases sorafenib-mediated ER stress and apoptosis in the cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. This mechanism may lead to a new therapeutic strategy in cholangiocarcinoma.
Keywords: intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, MANF, sorafenib, prognosis