108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

STAT3 诱导的 lncRNA CASC9 上调通过与 EZH2 相互作用并影响 PTEN 的表达,从而促进膀胱癌的进展
Authors Yuan B, Sun R, Du Y, Jia Z, Yao W, Yang J
Received 1 February 2020
Accepted for publication 29 July 2020
Published 16 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 9147—9157
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S248006
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
Objective: Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) cancer susceptibility candidate 9 (CASC9 ) has been reported to play a vital role in tumorigenesis. This study explored the biological role of CASC9 and its regulation mechanism in bladder cancer (BC).
Methods: Gene expression was evaluated using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and Western blot. The functional role of CASC9 in BC was studied using Cell Counting Kit-8, colony formation assay, scratch wound healing assay, transwell invasion assay, and xenograft tumor assay. In addition, the mechanism of CASC9 function in BC was determined using RNA immunoprecipitation assay and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay.
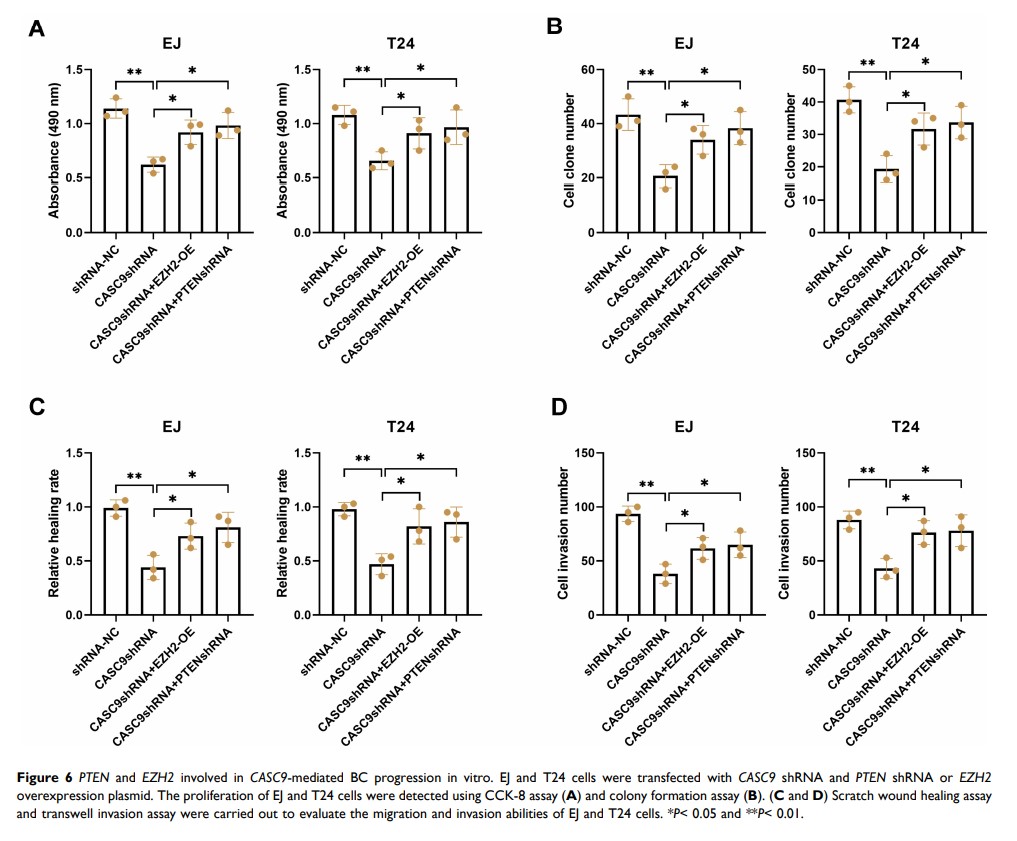
Results: CASC9 was upregulated in BC tissues and cell lines, and correlated with the staging and metastasis in BC. Knockdown of CASC9 inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of BC cells. Similarly, silencing of CASC9 inhibited tumor growth in vivo. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3 ) was upregulated in BC tissues and cell lines, and positively correlated with CASC9 in BC tissues. Moreover, CASC9 was shown to be regulated by STAT3 in BC cells. Furthermore, CASC9 regulated phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN ) expression by interacting with enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2 ). More significantly, CASC9 silencing-mediated inhibition of BC progression was partly reversed by EZH2 overexpression or PTEN inhibition.
Conclusion: Upregulation of CASC9 induced by STAT3 promoted the progression of BC by interacting with EZH2 and affecting the expression of PTEN , representing a novel regulatory mechanism for BC progression.
Keywords: bladder cancer, cancer susceptibility candidate 9 , signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 , phosphatase and tensin homolog , enhancer of zeste homolog 2