108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体通过抑制细胞焦亡保护心肌免受缺血/再灌注损伤
Authors Tang J, Jin L, Liu Y, Li L, Ma Y, Lu L, Ma J, Ding P, Yang X, Liu J, Yang J
Received 21 November 2019
Accepted for publication 25 July 2020
Published 16 September 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 3765—3775
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S239546
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
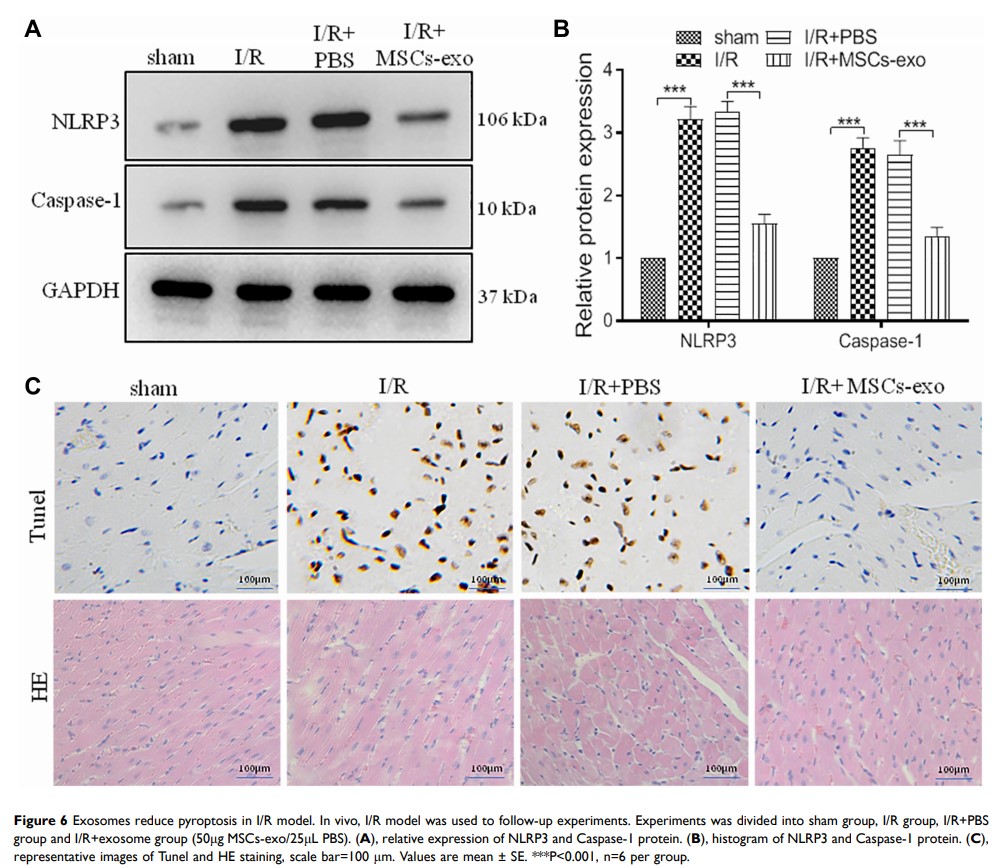
Objective: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) show unique advantages in cardiomyocyte repairment. Exosomes derived from MSCs can enhance the viability of myocardial cells after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury and regulate inflammation response. The study was designed to ascertain whether MSCs-exo protect the myocardium against I/R injury through inhibiting pyroptosis, and the underlying mechanisms.
Methods and Results: Experiments were carried out in H/R and I/R model. Cell viability was inhibited and NLRP3 and caspase1 protein levels were upregulated in H/R model. However, MSCs could inhibit cell apoptosis and pyroptosis in H/R model. Moreover, we used MSCs-exo to treated H/R model, and flow cytometric analysis results showed the inhibition function of MSCs-exo on cell apoptosis, and Western blot data suggested that NLRP3 and Caspase-1 expressions were downregulated in H/R model. Furthermore, exosomal miR-320b targeted NLRP3 protein, and MSCs-exo OE could inhibit NLRP3 expression and pyroptosis in H/R. In addition, the inhibition function of MSCs-exo on pyroptosis also was found in I/R model, and HE and Tunel staining also got similar results.
Conclusion: Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells could protect the myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibiting pyroptosis.
Keywords: exosome, mesenchymal stem cells, ischemia/reperfusion injury, pyroptosis, miR-320b