108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

腹腔镜肝切除术中超声引导下双侧腹横肌平面阻滞联合腹直肌鞘阻滞的术后镇痛效果:一项随机对照研究
Authors Lu X, Yu P, Ou C, Wang J, Zhou Z, Lai R
Received 15 June 2020
Accepted for publication 21 August 2020
Published 18 September 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 881—888
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S267735
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Background: Our aim was to investigate the postoperative analgesic effect of ultrasound (US)-guided bilateral transversus abdominis plane (TAP) blocks combined with rectus sheath blocks (RSBs) in laparoscopic hepatectomy.
Patients and Methods: A total of 126 patients were allocated into two groups for analysis. Group 1 (n = 63) did not receive any local anesthetics. Group 2 (n = 63) received US-guided bilateral TAP blocks and RSBs using 20 mL 0.25% ropivacaine in each block. Postoperative pain scores, the dose of intraoperative remifentanil, 24 h consumption of oxycodone, adverse events such as postoperative dizziness, nausea and vomiting, and the length of postoperative hospital stay were recorded.
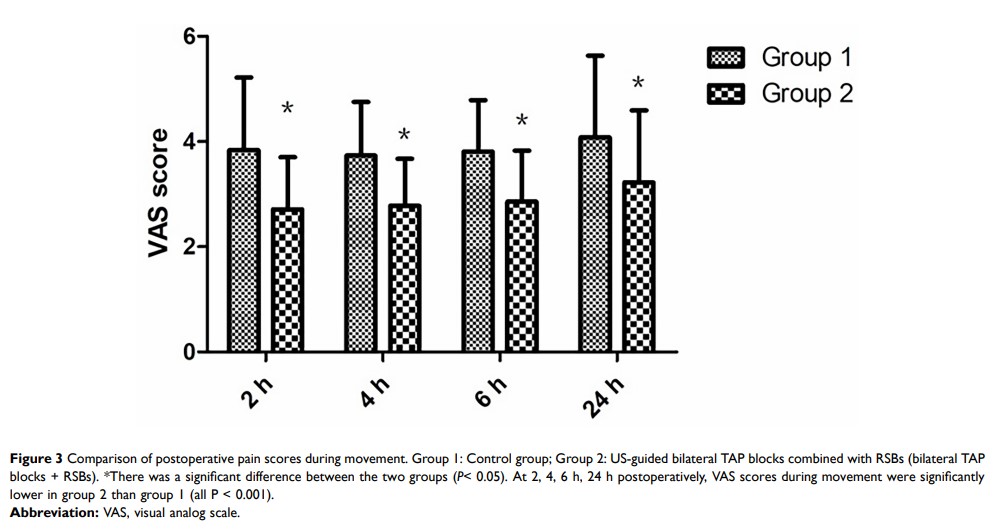
Results: In the postanesthesia care unit, patients in group 2 had significantly lower pain visual analog scale (VAS) scores at rest than those in group 1 (P < 0.001). The VAS scores both at rest and during movement were significantly lower in group 2 than in group 1 at 2, 4 and 6 h postoperatively (all P < 0.001). There was no difference in VAS scores between the two groups at rest 24 h postoperatively (P = 0.477). However, the VAS score during movement at 24 h in group 2 was significantly lower than that in group 1 (P < 0.001). No significant differences in the incidence of adverse events or the dose of intraoperative remifentanil were observed between the two groups (all P > 0.05). Patients in group 2 had a significantly lower 24 h consumption of oxycodone than patients in group 1 (P < 0.001). The mean length of postoperative hospital stay of group 2 was shorter than that of group 1 (P = 0.032).
Conclusion: US-guided bilateral TAP blocks combined with RSBs provide effective postoperative analgesia for laparoscopic hepatectomy, and they could shorten the postoperative hospital stay without increasing the incidence of adverse events from opioids.
Keywords: laparoscopic hepatectomy, analgesia, transversus abdominis plane block, rectus sheath block, ultrasound