108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

卧床休息对急性深静脉血栓形成患者的影响:一项定性研究
Authors Gong JM, Du JS, Han DM
Received 9 July 2020
Accepted for publication 2 September 2020
Published 18 September 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1659—1667
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S271481
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Background/Objective: The recommendation of bed rest for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) patients has changed during the last 20 years, and it has become a concern for researchers. The existing researches on potentially harmful treatment of bed rest for DVT patients focus only on physiological outcomes. This qualitative study explored the implications of bed rest from the perspective of patients with acute DVT. Understanding these implications will provide more evidence on whether bed rest should be used as a medical treatment of acute DVT.
Patients and Methods: For data collection, a descriptive qualitative design utilizing semi-structured, in-depth, face-to-face interviews with nine patients with acute DVT was conducted. In order to find the themes and subthemes emerging from the interviews for data analysis, the Colaizzi method, which was suggested by phenomenological methodology, was used.
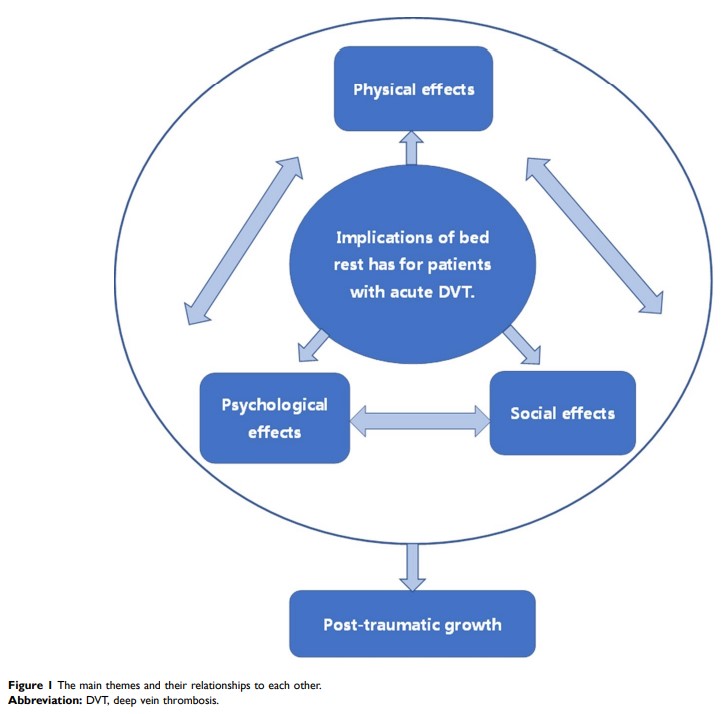
Results: The four major themes found were physical effects, psychological effects, social effects, and post-trauma growth. These themes illustrated the bed rest experiences of patients and it has a negative impact on the quality of life (QOL) amidst acute DVT.
Conclusion: Bed rest for patients with acute DVT is a physically, emotionally, and socially distressing phenomenon that simultaneously affects QOL and induces post-traumatic growth. We believe that bed rest is not beneficial to the physical and mental health of patients with acute DVT. This study adds to the available evidence on the harmful effect of bed rest as a treatment from the perspective of patients with acute DVT. Further quantitative studies should compare the quality of life and psychosocial status of patients with and without bed rest amidst acute DVT.
Keywords: bed rest, deep venous thromboembolism, qualitative, patient experience