108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PACE4 表达是鼻咽癌的一个新的独立预后因素
Authors Lin Y, Long H, Tan X, Zhang D, Jiang L
Received 28 May 2020
Accepted for publication 2 August 2020
Published 18 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 8623—8629
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S264143
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskaza
Background: Paired basic amino acid-cleaving enzyme 4 (PACE4) belongs to the family of proprotein convertase and is essential for tumor progression, whereas its role in cancer remains controversial and little is known about its role in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). The aim of this study was to examine if the expression of PACE4 is a prognostic biomarker for patients with NPC.
Methods: Immunofluorescence (IF) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) were used to analyze PACE4 expression in NPC cell line CNE1 and 172 clinicopathologically characterized NPC tissues. The data were analyzed by Chi-square test, Kaplan–Meier plots, and Cox proportional hazards regression model.
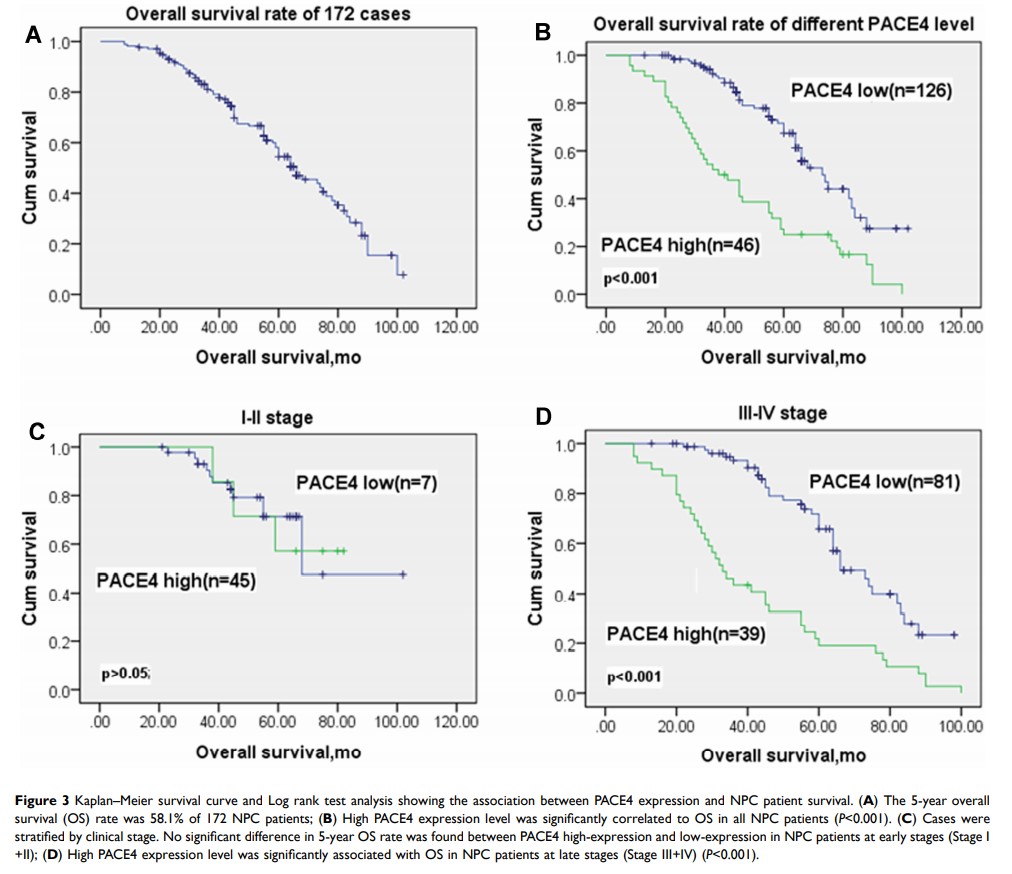
Results: IF and IHC staining results showed that PACE4 was mainly located in the cytoplasm of NPC cell line (CNE1) and NPC tissues. Expression of PACE4 was observed in 46/172 (26.7%) of NPC tissues. Further analysis showed that expression of PACE4 was positively associated with late N stage, distant metastasis, and late clinical stage (P < 0.05). High expression of PACE4 predicted shorter 5-year overall survival of patients with NPC, especially for the patients in advanced stage (32.7% vs 77.3%, P < 0.001). Furthermore, multivariate analysis showed that PACE4 expression may serve as a potential prognostic factor for NPC.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that PACE4 may play a crucial role in tumor progression and may serve as a valuable prognostic biomarker for patients with NPC.
Keywords: paired basic amino acid-cleaving enzyme 4, immunohistochemistry, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, overall survival, prognostic biomarker