108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-133a-3p 通过靶向 CORO1C 调节肝细胞癌的进展
Authors Han S, Ding X, Wang S, Xu L, Li W, Sun W
Received 19 March 2020
Accepted for publication 5 August 2020
Published 21 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 8685—8693
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S254617
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Introduction: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are key modulators for gene expression via inducing translational repression or target gene degradation. miR-133a-3p was reported to stimulate or inhibit cancer progression but its role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains to be explored.
Methods: Quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) was utilized to explore miR-133a-3p expression level in HCC cells. Dual-luciferase activity reporter assay was used to validate the direct interaction between miR-133a-3p and coronin-like actin-binding protein 1C (CORO1C). In addition, we analyzed the expression levels of miR-133a-3p and CORO1C in HCC tissues and normal tissues on the UCALAN website. Functional assays including cell counting kit-8 assay, colony formation assay, flow cytometry analysis and transwell invasion assay were conducted to explore the biological functions of miR-133a-3p in HCC.
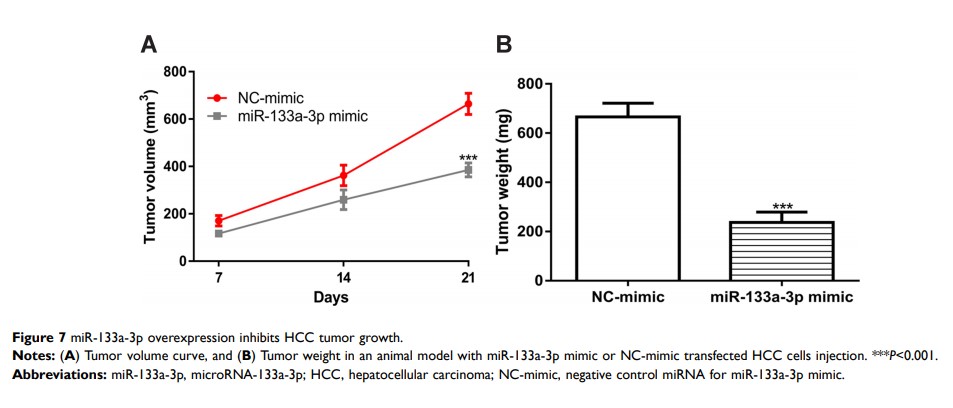
Results: miR-133a-3p was found to have downregulated expression in HCC tissues and cells. Meanwhile, we showed that low miR-133a-3p levels were correlated with poorer overall survival of HCC patients. Overexpression of miR-133a-3p suppressed HCC cell growth and invasion but promoted cell apoptosis via targeting CORO1C.
Discussion: Our results revealed a novel mechanism of miR-133a-3p in regulating HCC progression and provided evidence that miR-133a-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in HCC.
Keywords: miR-133a-3p, CORO1C, hepatocellular carcinoma, prognosis