108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CAV1 的表达升高与接受手术和新辅助化疗的乳腺癌患者的不良预后有关
Authors Ye JH, Shi JJ, Yin X, Wu HY, Xu XY, Yao YZ, Zhang WJ
Received 26 June 2020
Accepted for publication 8 September 2020
Published 22 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 8887—8892
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S264673
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
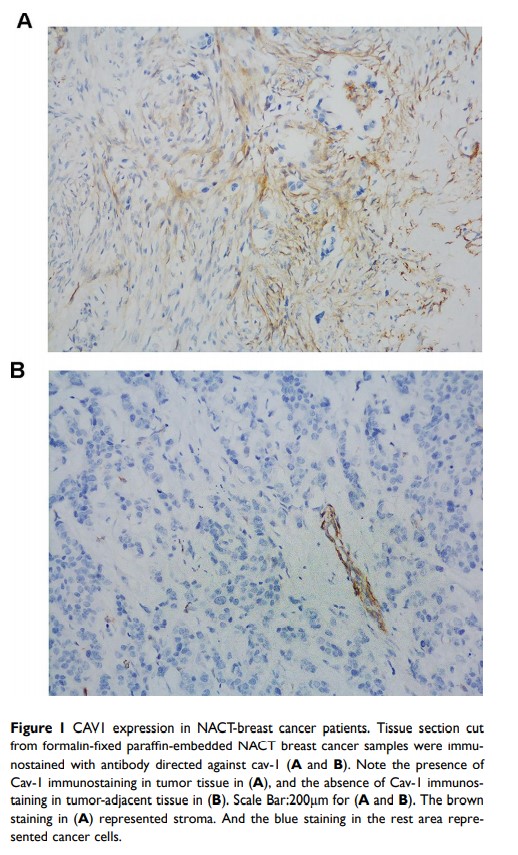
Introduction: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT), which is standard treatment for locally advanced breast cancer, improves the resectability of patients with early breast cancer and reduces the extent of breast and axillary surgery. Caveolin-1 (CAV1) is implicated in human cancers, although its utility for cancer prognosis is unknown. Here, we investigated the expression of CAV1 in breast cancer tissues to evaluate its prognostic significance on patients with breast cancer administered NACT.
Methods: CAV1 expression in 80 breast cancer tissue samples was evaluated using immunohistochemistry (IHC). The association between CAV1 levels and clinical factors was analyzed using the chi-square test and that between CAV1 and prognosis was evaluated using multivariate Cox regression and Kaplan–Meier analyses.
Results: High levels of CAV1 were significantly associated with survival, and patients with overexpression of CAV1 had a poor prognosis. Adjusted multivariate Cox regression analyses revealed that a high level of CAV1 expression was an independent, significant prognostic factor for patients with breast cancer treated with NACT.
Discussion: Overexpression of CAV1 in patients with breast cancer administered NACT was associated with shorter disease-free survival and overall survival. Therefore, high levels of CAV1 may serve as a prognostic biomarker for such patients.
Keywords: CAV1, IHC, clinical outcome, biomarker