108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PFTK1 下调可抑制非小细胞肺癌的迁移和侵袭
Authors Jiang M, Chen Q, Zhao X, Teng Y, Yin C, Yue W
Received 2 June 2020
Accepted for publication 20 August 2020
Published 22 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 9281—9289
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S265540
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: PFTK1, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase, plays pivotal roles in tumorigenesis. Cell motility and invasiveness could be enhanced by PFTK1 in various tumors. However, the function of PFTK1 in NSCLC metastasis remains unclear. In this study, the potential role of PFTK1 in NSCLC metastasis was determined.
Materials and Methods: In this study, the potential function of PFTK1 in lung cancer patients was analyzed with the Kaplan–Meier plotter database. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of PFTK1 was established in two NSCLC cell lines (H1299 and 95C) to explore the role of PFTK1 in NSCLC. The efficacy of downregulation of PFTK1 was examined by Western blot and immunofluorescence. The role of PFTK1 in cell migration and invasion ability was detected by wound healing and transwell assays. The protein levels in lung cancer cells were determined by Western blot. Immunofluorescence analysis was used to evaluate the structure of filamentous actin.
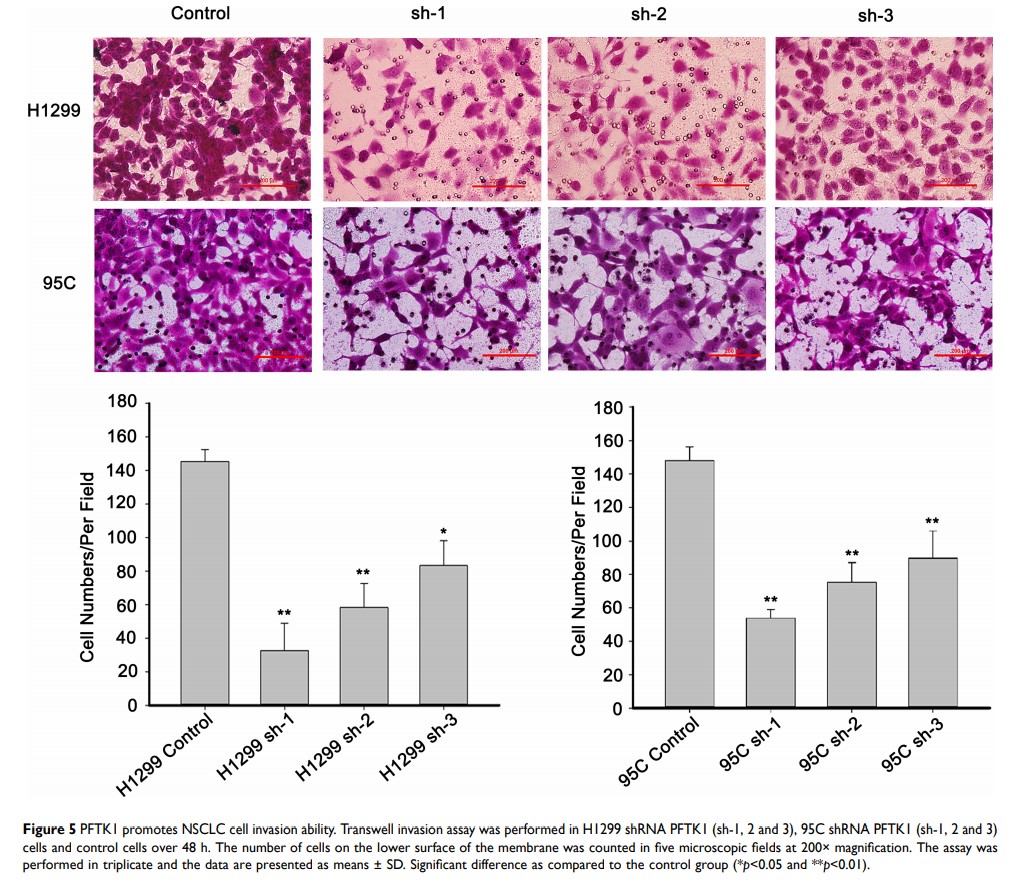
Results: Overexpression of PFTK1 was associated with the poor survival prognosis in NSCLC patients. PFTK1 knockdown cells were constructed successfully. Suppression of PFTK1 significantly inhibited the cell migration and invasion in H1299 and 95C cells. Notably, after PFTK1 downregulation, the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers vimentin, ZEB1 and β-catenin were obviously decreased. Additionally, immunofluorescence analysis indicated that PFTK1 downregulation remarkably induced filamentous actin depolymerization.
Conclusion: In summary, PFTK1 could significantly promote lung cancer metastasis through changing EMT progress and modulating intracellular cytoskeleton F-actin expression. Taken together, our findings indicated that PFTK1 might serve as a novel therapeutic target for the inhibition of NSCLC progression.
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer, PFTK1, invasion